The Ultimate Manual to Shared Google Drives Security
Shared Google Drive offers a collaborative cloud environment for teams to share, access, and store files. But every prudent administrator knows the risks inherent to these kinds of platforms. This guide covers everything you need to know about enhancing Shared Google Drive security, including how to get started securing shared drives.
What is Shared Google Drive Security Anyway?
Google Drive has proved indispensable in allowing employees to share, store, and access files remotely. With Google Drive, employees can work with office files, sync data across devices, share and organize files, backup documents, and collaborate with team members. In addition, this popular file storage and synchronization service have made it easier than ever to collaborate and share information within departments.
Shared drives group users together in one drive to enhance collaboration. Files in the shared drive belong to the organization rather than individuals. This scenario enables team members to share information from anywhere or from any device. It doesn’t even matter if members leave. The files remain in place and accessible to the team, and the admin can delete their accounts.
But employees are often working with sensitive files, data, and information. Sensitive data may include credit card numbers, bank account numbers, social security numbers, and identifiable medical information. Shared Google Drive security is concerned with protecting sensitive data in all states, whether at rest, in motion, or in use.
How Shared Google Drive Security Works
Google Drive secures your organization’s data in several ways. For example, Google encrypts data with 128-bit or 256-bit keys when a user uploads it to Google Drive. The company also protects data in transit with Transport Layer Security. This protection reduces the chances of cybercriminals intercepting data as it moves to and from Google Drive.
Additionally, Google Accounts have built-in security features to detect and block common threats like malware, phishing, and spam. Rest assured that more than 1,000 Google security engineers work around the clock to ensure that your data is safe.
Even so, Google Drive offers customizable security options to put you in control of your data security. For example, you can set permissions for who can or cannot share files externally. You can even disable copying, printing, or downloading for specific files. Thus, you have a lot of flexibility to manage your organization’s data shared Google Drive security.
As such, these customizable security options will be the focus of this guide. This way, you can get a full handle of your organization’s Google Drive security for corporate privacy and regulatory compliance.
Below are two real-world examples of shared Google Drive security scenarios to better understand the topic.
Example 1: Google Docs Users Become Victims of a Phishing Scam
In 2017, unknown cybercriminals executed a phishing campaign targeting random Google Docs users. During this campaign, users received an invitation to edit a Google Doc. However, unwitting users who clicked the link to open the document were redirected to a webpage purporting to be the genuine Google Docs service.
Then, users were prompted to grant the service access to their email accounts, contacts, and documents. The malware then emailed all contacts on the victim’s list, spreading even further. Fortunately, Google detected and stopped the threat within an hour. Additionally, the subsequent Google investigation reported that no information other than the victim’s contacts was compromised.
This incident highlights the importance of training staff on cyber hygiene. Similar scams have successfully obtained the victims’ Google Drive login credentials. This means that an employee could unwittingly grant cybercriminals access to an organization’s Google Drive. Such a situation could be disastrous, especially if the shared drive contains privileged, sensitive, or restricted information.
Federal laws such as the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) and Health Insurance Portability and Accounting Act (HIPPA) are designed specifically for these kinds of incidents. Your organization could easily face charges for failing to implement and maintain reasonable data security measures. Such a scenario could result in hefty fines or even losing your business license.
Example 2: Equifax Data Breach
Equifax, one of America’s largest consumer credit reporting agencies, was hacked in September 2017. The cybercriminals made off with the personal data of more than 209,000 consumers, including credit card numbers, phone numbers, home addresses, names, and social security numbers.
Equifax chose to settle for $1 billion after a drawn-out court case. Equifax also pledged to invest $1 billion in security updates following the breach. Four members of China’s military were indicted in connection with the violation.
Such breaches are an ever-present possibility in shared Google Drives. For example, just a single compromised Google Workplace account can jeopardize the shared drive’s security. Additionally, there’s always the possibility that employees might accidentally share sensitive information with outsiders.
You can avoid these scenarios and other data breach situations by enhancing security for shared drives. Google Workplace offers admins a set of controls to improve data security.
How to Get Started With Shared Google Drives Security
It is impossible to overstate the importance of shared drives security. Granting file access to multiple people increases the risk of unauthorized access. Here’s how you can get started securing shared drives.
Step 1: Upgrade Your Plan
Google Drive is a very secure service to begin with. But if you’re on the Google Workspace (formerly G Suite) business starter plan, it’s worth upgrading to the business or enterprise plans for its added security features. The extra security features are worth the additional cost.
For example, the Business Plus plan offers security features not available with the Starter or Standard plans. In it, you’ll get access to Google Vault, which helps to manage your organization’s data across all platforms, including Drive, Groups, Gmail, Hangouts Chat, and Hangouts Meet. This way, you’ll be able to store an extensive chat history and retrieve old emails and documentation. Of course, you’ll be grateful for this functionality in case of legal issues.
You can up the ante by upgrading to the enterprise plan. Enterprise plans come with data loss prevention (DLP). This feature allows admins to set up rules to detect sensitive information and content. Additionally, admins can determine what happens if someone gains access to or attempts to share specific files outside the organization.
Moreover, the Enterprise plan has BigQuery, a feature that allows admins to monitor employee behavior and activity via log queries. Also, Enterprise users have access to the Security Center. Here, admins can watch external file sharing and even detect potential security threats before they happen.
Other nice-to-have security features exclusive to the Enterprise plan include:
- Access transparency
- S/MME encryption
- Context-aware access
- Cloud identity premium
You don’t have to upgrade all employee accounts. Google Workplace allows you to assign different plans to different users. This way, you can save costs and grant each user the appropriate level of control and permissions.
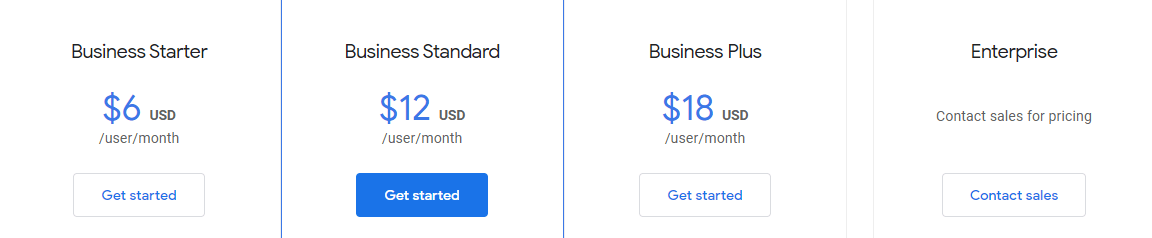
Google Workplace pricing plans are as follows:
- Business Starter – $6 per user per month
- Business Standard – $12 per user per month
- Business Plus – $18 per user per month
- Enterprise – Custom pricing, contact the sales team.
Step 2: Change Shared Google Drive Settings
It often happens that the company’s default Google Drive settings apply to all shared drives as well. For example, it might be the case that full-access users can modify the Shared Drive settings. So, review the settings to allow or restrict access appropriately. These changes will also apply to all Shared Drives.
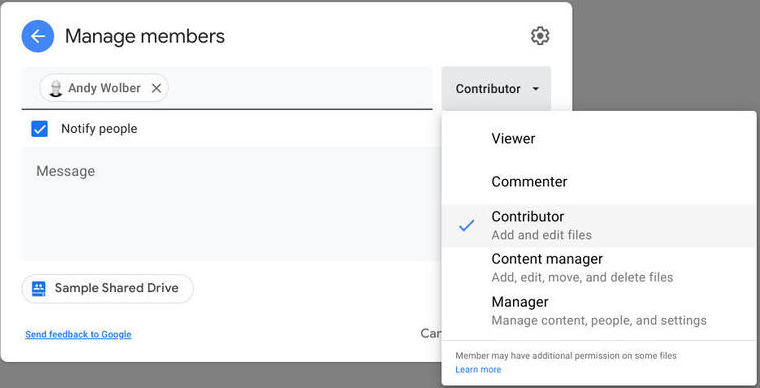
Google Drive provides five roles with varying levels of access. For instance:
- Viewer–Only allows members to view content
- Commenter – Users with this role can view and comment on content
- Contributor/Editor –Can add, comment, and edit files
- Content Manager – Can add, comment, move, and edit files, as well as add people and groups to files in the shared drive
- Manager – Can manage people, content, and settings, as well as all shared drive features
The roles you choose to assign team members entirely depend on your organization. Some admins use the principle of least privilege. In this case, members are appointed viewer or commenter status with restricted access to adding, removing, sharing, or altering content on shared drives.
Alternatively, many organizations prefer to assign members contributor roles. Users will be able to add content as well as view and comment on shared content. This designation allows for a good compromise since the users won’t change or rearrange files or folders in the shared drive.
You can assign roles by clicking Drive > Manage shared drives > Shared drives access levels.
You can also monitor the effects of the change and adjust your security policy accordingly. You may find that your policy is too restrictive or too lax. In any case, it is prudent to grant access on a need-to-know basis. Err on the side of caution and loosen up restrictions only when necessary.
Step 3: Enforce Two-Factor Verification for All Account Users
A password may not be enough to protect your Google Drive account. Also, not all employees are prudent at picking solid passwords. So, two-factor (2FA) can help protect your shared drives, even if a threat actor gets their hands on members’ passwords.
Two-factor authentication requires you to provide two pieces of information to access your account. This information may include a password and a verification code. Google Drive allows administrators to enforce 2FA for all members on the shared drive. In this case, users who aren’t enrolled won’t be able to access their accounts.
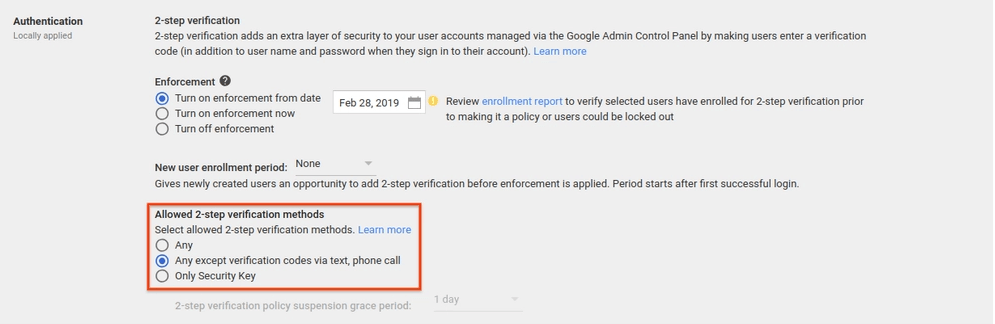
To enforce 2FA:
- Log in to the Google Admin Console
- Go to Security > 2-Step Verification
- Then, choose an organizational unit on the left side
- Click Allow users to turn on 2-step verification
- Finally, go to Enforcement and select when you’d like it to begin.
You can choose to enforce 2FA immediately or at any time in six months. Team members will see a reminder to enroll for two-step verification when they access their accounts.
It is a good idea to have a grace period for new members. A week is enough to ensure all new team members have enabled two-factor authentication. Also, it is worth using Google Authenticator or Google Prompt for verification. Cybercriminals can sometimes redirect phone numbers to another provider to gain access to verification codes.
Step 4: Determine Which Devices Can Access Shared Drives
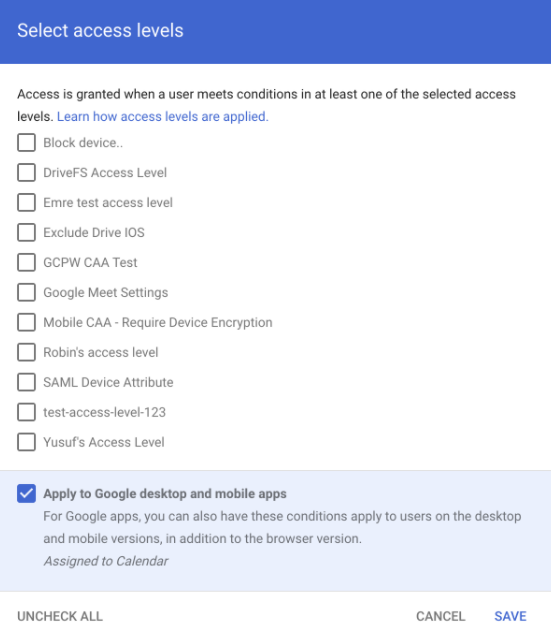
Take advantage of the Context-Aware Access feature to get tighter control of devices that can access shared Google Drives. Full-access members have control over where, when, and how team members can access shared drives.
For example, admins can authorize access only to company-issued devices. Similarly, admins can restrict access to apps outside of the organization’s network. It is even possible to combine conditions and values. For instance, you can set a policy where only encrypted devices within a specified IP range can access shared drives.
Admins also have the flexibility to set different access levels based on the user’s identity or the condition of their request.
You’ll first need to turn on Endpoint Verification in the admin console. Then, deploy the Endpoint Verification extensions to all company devices. Finally, go to Security > Context-Aware Access to create access levels.
Be sure to share your security policy with all team members. This way, nobody will be locked out at a crucial moment. Also, not all employees will be happy with the new restrictions. You can gain employee buy-in by training users on the importance of securing shared drives.
Step 5: Monitor Shared Google Drive Changes
Admins often have a hard time keeping up with changes in shared drives. This is especially true if there are full-access members with rights to modify the drive’s contents or settings. Admins have access to reports of all Shared Drives administrative activity within the organization.
To monitor changes to Shared Drives, simply log into the admin console. Then, navigate to Reports > Audit > Drive and choose the team drive you’d like to monitor. You’ll have access to all changes made to the team drive, complete with who made the changes.
You’ll also be able to track specific changes within the drive. For example, you can use the search filter to see which files can be shared externally that were previously only accessible from within the organization.
Protect your Google Drive with Real-time Access Control
Need a faster, easier way to secure all your sensitive documents?
Nira provides visibility and management over who has access to company documents in Google Workspace, with more integrations coming soon.
We offer a single source of truth and real-time monitoring so access control tasks that used to take hours now take a few minutes. We work with companies of all sizes, and our largest clients have millions of documents in their Google Workspace.
Nira offers speed, (our setup takes two minutes), security (it’s our highest priority), and scalability (we’ll support you as you grow).

