Using Google Vault for Data Retention
Data retention is a crucial element of business operations, requiring support to ensure its successful implementation. Enter Google Vault, a cloud-based solution offered by Google Workspace. Used to manage and preserve valuable data, Vault serves as a robust information governance and eDiscovery tool for organizations of all sizes. But how exactly does Google Vault aid with data retention?
Vault acts as a secure repository, enabling businesses to retain and access essential data, such as emails, chat messages, and files stored in Google Drive. Its significance lies in its ability to address several key aspects of data retention including compliance and legal requirements, as well as industry regulations.
Various US laws and industry compliance frameworks deal with data retention, including HIPAA, SOX, PCI DSS, and ISO. For example, according to HIPAA, health information needs to be kept for at least six years from the time it was created. Meanwhile, SOX states that any important documents related to auditing and reviewing financial statements must be kept for seven years after an audit or review is done.
Google Vault helps companies easily follow data retention policies and protect customer information. It also aids organizations in specific industries that have their own guidelines or contractual obligations. Compliance with these regulations helps companies build trust and demonstrate their commitment to data privacy.
In this post, we’ll cover how data retention works in Google Vault and how to set default and custom retention rules for organizations, helping them to reduce risk, ensure regulatory compliance, and foster a secure environment for company data.
How Vault retention works
In Google Vault, administrators can keep data for as long as is needed or remove it when maintaining the data is no longer necessary. Admins can change the settings to retain files even after they are deleted by employees or employees empty their Trash.
They can also set retention rules to automatically delete data after a certain period of time and remove it from all user accounts and Google systems. However, they should be extremely careful when configuring retention rules, as important information could be immediately and permanently deleted.
Please note: Google’s default settings require that data stays in Workspace indefinitely until an administrator or user deletes it. In Google’s updated Data Retention Policy, end users’ Drive files in the Trash will be deleted after 30 days. However, in Workspace, admins will be able to restore items deleted from a user’s trash for up to 25 days.
What data can Vault retain from each service?
Using Vault, the following data can be retained across different Google Workspace services:
Gmail: All emails that users send, receive, or draft, as well as their attachments. Vault can also retain confidential mode messages sent by users in the organization.
Google Groups: Messages and their attachments in groups sent when conversation history is turned on.
Google Drive: Files in users’ Drives and shared drives; files encrypted with Google Workspace client-side encryption; Google Meet data (unless Meet-specific retention has been turned on.)
Google Chat: Messages and their attachments sent with history on in Chat; DMs sent by external users to the organization’s users; messages sent by external users in the organization’s group messages and spaces.
Google Voice: Text messages, call logs, and voicemails and their transcripts.
For information on Google Sites, visit here. For Google Meet, visit here.
Default retention vs. Custom retention rules
In Vault, administrators can set two types of retention rules: custom and default. So, how do they know which one to use?
Default retention rules
A default retention rule is used when organizations need to keep all company data for all licensed accounts for a set period of time. This means that administrators can’t apply default retention rules to only specific accounts or time periods.
Remember, companies can have only one default retention rule per service, and it only applies to files in Drive that aren’t covered by a custom rule or hold.
Custom retention rules
If administrators must keep specific data for a set time, they should set a custom retention rule. They can specify the data with conditions and terms depending on the service:
- Gmail and Groups: Set by organizational unit, date ranges, and specific search terms.
- Drive, Meet, and Sites: Set by organizational unit and define expiration based on last modified dates and created dates, trashed dates, or Drive label date fields. Choosing dates based on when documents were last modified addresses the issue of stale documents. Meanwhile, setting custom rules by when documents were created helps with compliance requirements.
- Chat: Set by organizational unit or for all Chat spaces in the organization.
- Google Voice for Google Workspace: Set by organizational unit and data type.
How to set a custom retention rule
- Visit vault.google.com
- Go to “Retention”> “Custom Rules”> “Create.”
- Click “Drive” and “Continue.”
- Choose from an organizational unit, all shared drives, or specific shared drives: Admins can choose from an organizational unit such as Sales, Marketing, etc., and then they have the additional option of including shared drives by selecting “Include results from shared drives.”
- They can choose to include all shared drives in their organization.
- They can select shared drives from specific accounts. They can enter the names of one or more accounts and click “Find.” Select one or more shared drives and click “Add.”
- Click “Continue.”
- Choose how long to keep the files:
- If they select “Indefinitely,” they will permanently retain documents under this rule.
- If they select “Retention period,” they can choose a number of days to retain their documents and select the reference time for the start of the period.
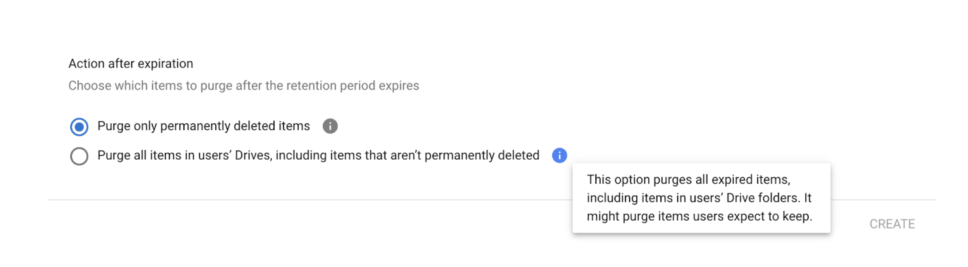
9. Decide what to do with files after the retention period:
- They can choose option one in the modal to remove only the files that are already emptied from the users’ Trash folder.
- They can choose option two in the modal to remove all files, including files that aren’t deleted.
10 . Click “Create.”
11. For accounts with a retention period, admins must confirm that they understand the rule’s effects. Check the boxes and click “Accept” to create the retention rule.
How to set a default retention rule
- Visit vault.google.com.
- Click “Retention.”
- Click “Drive.”
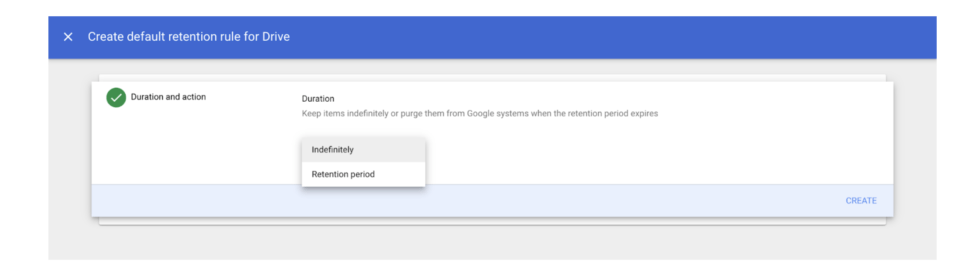
- Choose how long to keep files:
- If they select “Indefinitely,” they will permanently retain documents under this rule.
- If they select “Retention period,” they can choose a number of days to retain their documents and select the time for the start of the period.
5. Decide what to do with files after the retention period
- Choose option one in the modal to remove only the files that are already emptied from the users’ Trash folder.
- Choose option two in the modal to remove all files, including files that aren’t deleted.
6. Click “Save.” Admins must then confirm that they understand the rule’s effects. Check the boxes and click “Accept,” to save the retention rule.
Google Vault not only offers a way to manage data retention but also enables companies to establish and enforce retention policies tailored to their specific needs. By leveraging this solution, organizations can ensure that data is retained for the necessary duration and disposed of appropriately when it is no longer required.
The ability to set custom or default retention rules empowers businesses to strike a balance between retaining critical information for compliance and legal purposes while disposing of unnecessary data to optimize storage resources. This streamlined approach not only bolsters data integrity but also helps organizations reduce storage costs and enhance overall data management efficiency.
For further information on how to use Google Vault for data retention, compliance, and more, check out our comprehensive guide.

