Auditing in Google Vault: Everything You Need to Know
Companies encounter escalating security challenges when managing their data. For help, organizations are turning to Google Vault—a cloud-based investigation and legal hold solution for those using Google Workspace.
This powerful tool lets businesses retain, search, and export data, including emails, chat messages, and more. As data protection becomes increasingly critical to business operations, Google Vault offers a solution to navigate the complexities of information governance and electronic discovery.
Auditing is crucial to ensure that Vault is used responsibly and in compliance with company policies and external regulations.
Vault gives users a large amount of power, which could be abused, for example in the case of a breach where a Vault administrator’s account was compromised. In the unfortunate event of a breach or unauthorized access to Vault, the audit log becomes a valuable resource. Administrators can analyze the log to determine the sequence of events, identify any suspicious activities, and pinpoint the individuals involved in the incident.
Google Vault also helps in instances of litigation or security investigations. During legal proceedings, when a court orders the process of discovery, both parties are obligated to produce all relevant documents and information. This may include not only Vault user activity audit logs but also other data types including emails, chat records, and files.
If companies have a legal issue, and Vault was used to put data on a hold, administrators can generate an audit report to showcase what was done in Vault. Audit trails allow them to see and show searches, exports, content views, and more.
Compliance is also a significant driver for auditing Vault user activity. Numerous industries and organizations are bound by regulations mandating the auditing of user activity within their systems. Vault’s audit log is instrumental in helping companies comply with these regulations by providing a comprehensive record of user actions and access to sensitive data.
In this post, we’ll go over how to audit Vault user activity, including activity across all of Vault or activity pertaining to a particular issue. We’ll also explore what audit logs contain and how long the data persists.
How to audit Vault user activity
In Vault, administrators can examine the actions performed by Vault users. This can be done either on a comprehensive level encompassing all of Vault or by focusing on a particular case. For instance, administrators can conduct an audit across Vault to identify the users who made modifications to retention rules. Or, they can perform an audit on a specific case to determine the individuals who accessed export files related to that particular issue.
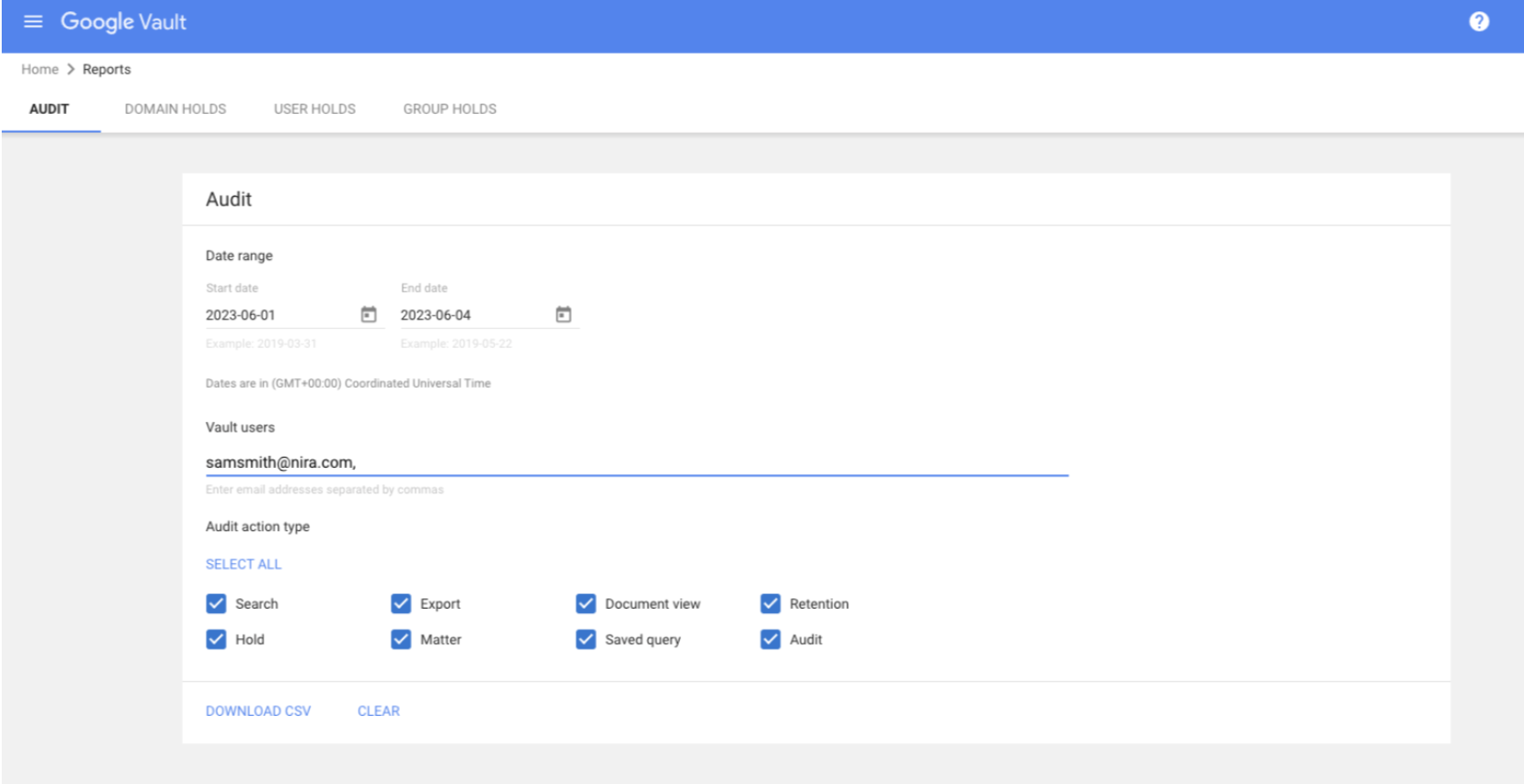
How to audit user activity across all of Vault
- Sign in to vault.google.com.
- Click “Reports.”
- Administrators have the option to select a date range.
- They also have the option to enter the email addresses of Vault users they want to audit. They can leave this field blank if they want to audit the actions of all Vault users.
- They can select what types of Vault user actions to audit.
- Click “Select all” to audit all actions.
- Or check the box of each action to audit.
- Click “Download CSV” to receive a CSV file of the audit information.
- Open the CSV file in a spreadsheet app, such as Google Sheets.
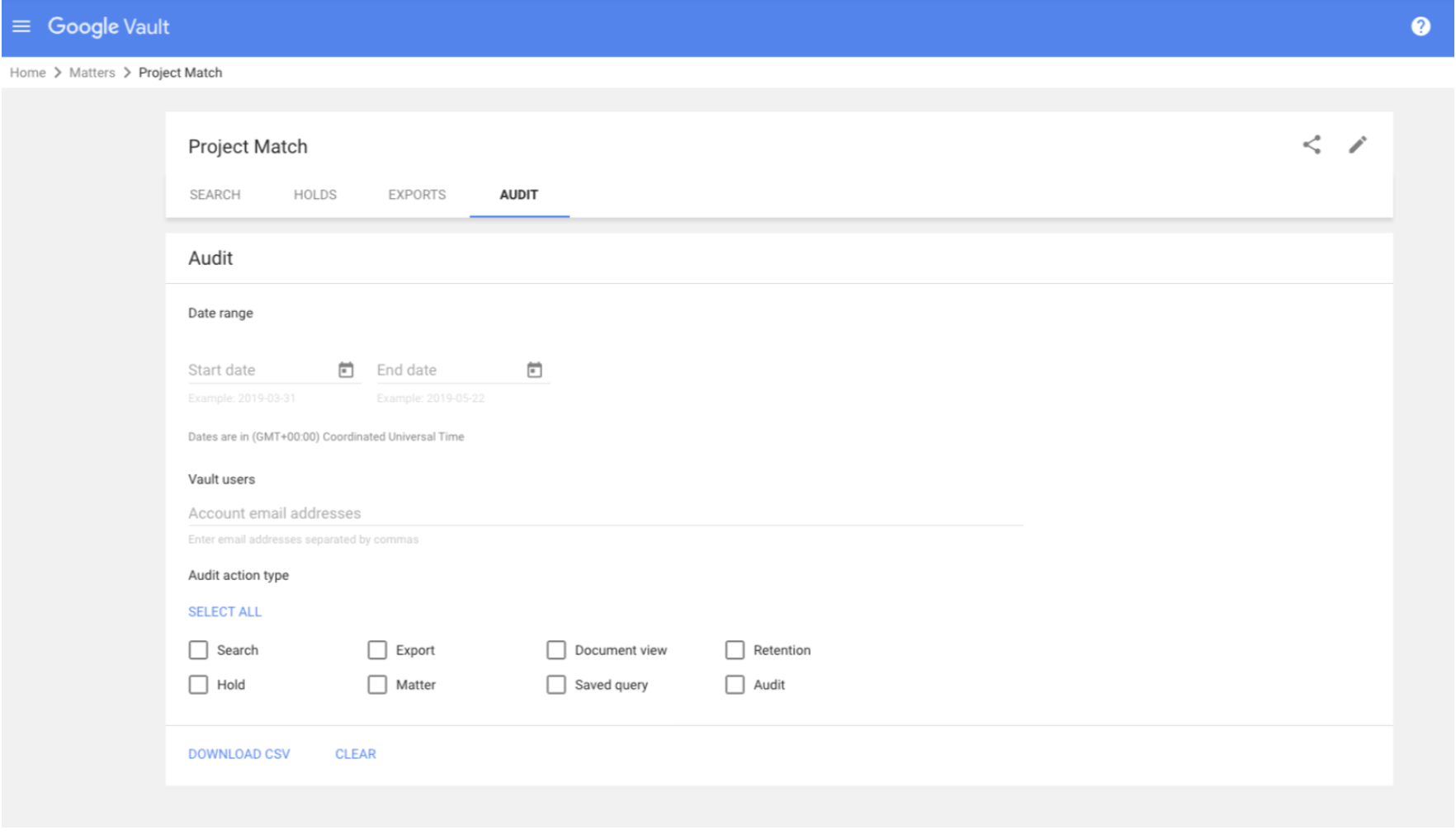
How to Audit activity in a specific matter
In Vault, a matter provides a place to organize the holds, searches, and exports related to an eDiscovery project. Here’s how to audit Vault activity in a specific matter.
- Sign in to vault.google.com.
- Click “Matters.”
- From the list of matters, click the matter that needs to be audited.
- Click “Audit.”
- Administrators have the option to select a date range.
- They also have the option to enter the email addresses of Vault users to audit. They can leave this field blank to audit the actions of all Vault users.
- Admins can select the types of Vault user actions that should be audited.
- Click “Select all” to audit all actions.
- Or check the box of each action to audit. Please note: No retention rule-related actions are reported for matter-specific audits.
- Click “Download CSV” to receive a CSV file of the audit information.
- Open the CSV file in a spreadsheet app, such as Google Sheets.
What audits contain
Vault audit logs are unalterable, ensuring no one can change them, so administrators get an accurate picture of Vault user actions. These immutable logs can be downloaded as CSV files, allowing administrators to easily review them.
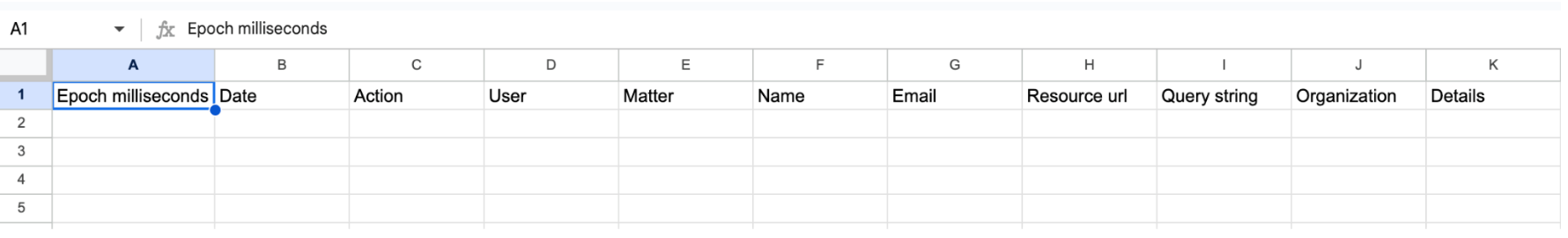
Audit logs contain the following information:
- Epoch milliseconds: This is the time that an action occurred in epoch milliseconds—the number of milliseconds that have elapsed since January 1, 1970 (midnight UTC/GMT).
- Date: The time that an action occurred in human-readable time. The time zone is always Pacific (–0700 or –0800).
- Action: The action that occurred. For example, EXPORT is logged whenever someone runs an export. Or VIEW_INVESTIGATION is logged when someone opens the Search or Export pages in a matter.
- User: The email address of the Vault user who performed the action in the Action value.
- Matter: For actions in a specific matter, the unique ID of the matter.
- Name: This information depends on the action the user took.
- If they viewed a document, it will show the unique ID of the document.
- If they removed or added a collaborator, it will show the email address of the user who was added or removed.
- If the user created an export in a matter, the name of the export.
- Email: The email address of the collaborator who was added to or removed from a matter.
- Resource URL: The URL of any document that the user viewed.
- Query string: The search parameters the user entered for a specific search.
- Organization: The name of the organizational unit to which the action applies.
- Details: The retention period in days that a user set for a custom retention rule. The period is indicated as “Period: # days.”
How long does the information in audit logs persist?
Actions in audit reports can’t be deleted by Google or by any Vault administrator or user as long as an organization continues to use Vault. If an organization terminates its Vault service, audit data is deleted after approximately 30 days.
Google Vault is a powerful tool for managing and safeguarding an organization’s critical data. By proactively managing Google Vault, organizations bolster their data security posture and demonstrate a commitment to responsible data handling.
Administrators can audit the use of Google Vault within their organization, ensuring that only authorized individuals are utilizing the tool, and as intended. Given the extensive range of information available in Vault, it is crucial to perform regular audits to track the activities of Vault users, but only as needed.
The ability to audit Google Vault ensures that sensitive and confidential information remains protected. Administrators can also set permissions, granting access only to those who genuinely require access to the data. This approach minimizes risk, bolstering the organization’s overall data security posture. To learn more about auditing and access control in Google Vault, download our complete guide.

