The Complete Guide to IBM Cloud Security
How secure is IBM Cloud? How good is IBM Cloud Security?
As people browse their options for secure cloud service providers, they should at least consider Big Blue.
International Business Machines Corporation, better known to the world for more than a century as IBM, has an extensive set of solutions for protecting data, workloads, and other cloud assets. They offer individual purpose-built tools to address key vulnerabilities, as well as IBM Cloud Security services that centralize defensive operations across an organization.
In this post, we’ll cover the core capabilities of IBM Cloud Security, whether you are using the services to protect an on-premises, hybrid, IBM Cloud, or public cloud deployment.
We’ll also look at what separates IBM from its competitors. For companies with complex deployments and stiff compliance concerns, there may be no better option on the market.
Overview of IBM Cloud Security
No matter what provider you choose, keeping today’s distributed cloud workplace safe involves an organization-wide strategy and a suite of tools to protect every layer and endpoint.
IBM Cloud Security provides a rich set of services that are built to integrate directly into a dev-sec-ops workflow.
You’ll get access to many familiar kinds of services (data protection, secure access management, network traffic monitoring, etc.), but how they fit together as a whole is what distinguishes IBM Cloud Security from the pack.
Many companies actually report that they lose visibility as they increase the number of cloud security tools they employ. Everything is better protected in theory, but in practice, their IT team can’t separate meaningful signals from the constant noise generated across their cloud security arsenal.
With IBM Cloud Security, you can build out exactly the protections you need. As you add services, you can continue to manage them from a centralized console, bringing real-time, legible information to bear.
Both your IT team and developers will have actionable intelligence to move forward. For IT security professionals, it will be easier to detect and correct threats across the ecosystem. For developers, the threat knowledge will help them architect more secure applications.
In short, IBM has designed a suite of tools that make it easier for organizations to take a proactive approach to cloud security.
Let’s go through the major features of the key tools, and then talk about how companies can fit them together to optimize their cloud security posture.
IBM Cloud Security features and services
The specific blend of different IBM Cloud Security Services a company will need depends on their current deployment and future goals.
Like other cloud service providers, IBM has a shared responsibility model when it comes to cloud security.The level of customer responsibility changes depending on the service.
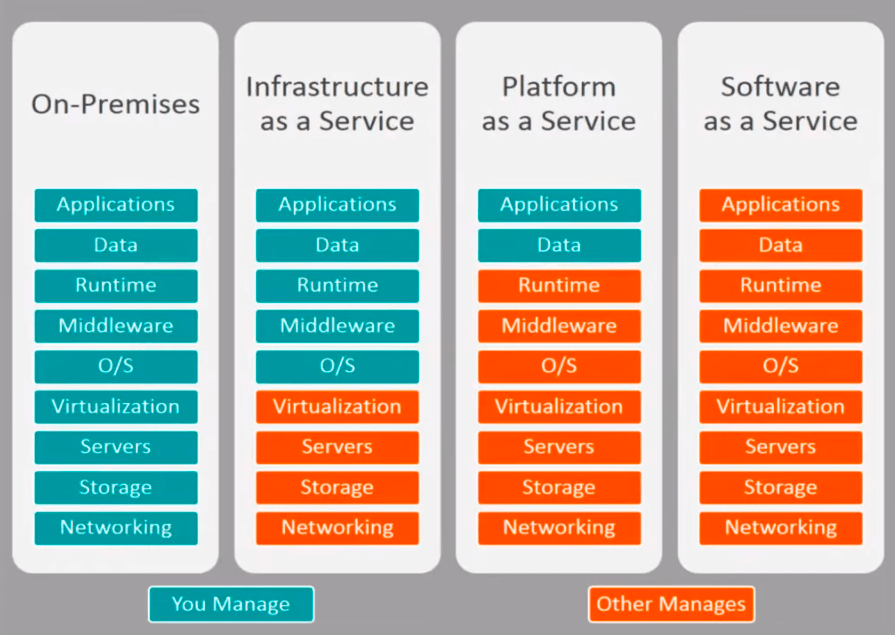
Companies using IBM Cloud Virtual Servers (or another public cloud IaaS) have to manage security from the operating system up. When they use IBM SaaS apps, on the other hand, the company handles everything from the application layer on down.
The more complex and varied the cloud services they require, the larger their attack surface, and the more tools they will need. That said, all companies that operate in the cloud need to address the following areas:
- Data security
- Identity and access management
- Network protection
- Security posture and compliance management
- Threat management
- Workload protection, integrated with DevSecOps
Let’s look at how IBM Cloud Security can help in each domain.
Data security
To protect against the loss, unauthorized access, or unauthorized use of cloud assets, IBM provides clients tools for:
- Data encryption
- Key management
- Certification management
With IBM Cloud Security, you have multiple options for encrypting your data at rest, in transit, and in use. This is true for any data storage type—block, files, databases, data services, objects—as well as any mix of on-premise, private, hybrid, or public cloud environments.
Data encryption tools
The core tool is IBM Multi-Cloud Data Encryption (MDE), which lets administrators provision, deploy and manage all instances of the product’s encryption agents across the company’s entire cloud ecosystem. It’s deployed as a virtual appliance, and you can host it on-premises, if you want, to ensure that keys are never in the cloud.
MDE works in many languages, and everything can be managed from a central console via the API with minimal scripting experience necessary. Essentially, it gives you the ability to easily encrypt data at scale, no matter where it lives.
IBM Cloud Security secures data at rest and in transit with similar encryption levels as other cloud service providers (quantum-resilient AES-256 for data at rest, SSL/TLS and HTTPS for data in transit), but they also offer hardware-driven solutions for encrypting data in use.
This is huge, because runtime memory may contain sensitive information and it is rarely encrypted. IBM Cloud Data Shield protects data while it’s in use for containerized workloads like Kubernetes or RedHat OpenShift.
You can leverage MDE’s real-time logging capabilities by integrating it with your key management system, IdP and SIEM. Get alerts about suspicious activity, and provide an additional layer of role-based access control that only allows appropriate users to decrypt data.
Additionally, you can set up privileged access control policies that allow admins and root users to access resources without seeing clear text data. This allows for the oversight key personnel need without increasing the risk of data loss or theft.
Key management
IBM Key Protect is the key management system for IBM Cloud Security. Acros all of your services, you can manage data encryption and the entire key lifecycle from a centralized console.
Customers who need additional levels of key security and auditing functions can use a IBM Cloud Hardware Security Module and Hyper Protect Crypto Services, which let you bring and keep your own keys.
Certificate management
IBM Cloud Certificate Manager is a secure repository for all of the certificates, their associated private keys, and third-party issued certificates. It allows centralized management across multi-cloud architectures, and will automatically notify you if certificates are going to expire.
The intuitive feature also integrates with IBM Cloud Container Service, so you can deploy custom TLS certificates to Kubernetes clusters.
Identity and access management
IBM Cloud Security simplifies the task of identity and access management (IAM), giving administrators a better view of their entire organization, user activity, and the ability to set flexible policies.
IBM Security Verify is the heart of IAM for IBM Cloud Security. From here, you can get granular control over permissions and roles for all your cloud microservices for employees as well as B2B, and B2C users. Security Verify comes with tools to enable:
- SSO: Single sign-on from any device to any application
- MFA: Multiple factor authentication for cloud, mobile, operating systems, VPNs, and web.
- Adaptive Access: Enforce MFA based on AI-powered risk assessment.
The result is greatly enhanced cloud security with minimal disruption to valid users. IBM Security Verify can also generate reports, providing admins with insights into potential vulnerabilities.
IBM Cloud App ID allows you to authenticate users on web, mobile, and native-cloud applications. Without code or redeployment, you can add SSO and MFA with user-defined password policies to all of your apps.
Both Security Verify and Cloud App ID are compliant with major regulations and easy to scale.
Network protection
Proper network configuration goes a long way towards hardening your cloud environment, but it’s not easy in today’s world. IBM’s network security services provide administrators with a complete view of their cloud ecosystem and the tools to control configurations.
Along with the traditional firewall and virtual firewall technologies offered by every cloud service provider, IBM has advanced solutions that streamline the process of securing your network.
IBM Cloud Security Groups are a set of five-tuple IP filter rules that you can enact to control traffic to and from public and private interfaces of a virtual server instance. It’s like an instance-level firewall that costs nothing to deploy.
For hybrid environments, IBM Cloud Direct Link lets you connect and add resources to your on-prem data centers. It provides consistent performance and scalable connection capacity allowing companies to grow their operations without public cloud exposure.
The FortiGate Security Appliance is a next-generation, high throughput firewall that you can leverage in the cloud. It enhances cloud-native firewall security by delivering superior, hardware-accelerated performance, and there is no hypervisor for attackers to target.
Threat detection and response
The IBM QRadar family of products helps the IT security team make sense of all the information captured by the data security, IAM, and network protection tools. They include:
- IBM QRadar SIEM
- IBM QRadar on Cloud
- IBM QRadar Advisor with Watson
- IBM QRadar User Behavior Analytics
- IBM QRadar Network Insights
- IBM QRadar Vulnerability Manager
- IBM QRadar Incident Forensics
- IBM QRadar Data Store
They tie into your other services, scanning millions of events captured in logs, flows, and behavior, looking for potential incidents. When something is detected, a prioritized, high-fidelity alert is provided automatically.
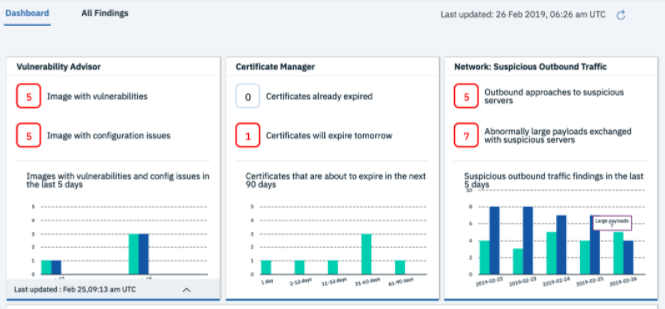
IBM Security Advisor centralizes cybersecurity operations for the entire enterprise in a single console. You get greater visibility into the things you care about, and the ability to detect and remediate problems across all of your different technologies and services.
They also have a range of threat intelligence offerings, like IBM X-Force Exchange. This is a free, cloud-based platform that gives your security operations a window into emerging threats. Find out what latest vulnerabilities and enhance your security by incorporating new fixes before facing an attack.
One of the nice things about IBM Cloud Security is that the tools can be used in concert with those from other cloud security companies, like Akamai and Check Point Software. The easy integration means you can keep the tools you already trust.
What differentiates IBM from other cloud security solutions?
In terms of cloud compute market share, IBM is not a dominant player. It’s far smaller than both AWS and Azure, and has been leap-frogged by Google Cloud Platform over the past few years. The big three public cloud service providers each come with built in security solutions that are very good, but some of the responsibility is always left to the customer.
What makes IBM different is that they seem more committed to letting customers work in the cloud however they want, rather than trying to draw consumers toward their cloud compute products.
The strength of IBM Cloud Security lies in the range of hardware, software, and cloud services they offer. These integrate well—with one another and third-party products—to provide insight and functionality across even the most complex architectures.
They have strategic alliances with AWS and Google Cloud Platform, which provide for complete end-to-end security across multi-cloud environments.
Companies don’t have to begin a complete transition to the cloud with IBM, let alone the public cloud. Instead, they can continue to build out both their on-premises and cloud assets with total confidence.
Who should consider IBM Cloud Security?
Anyone can benefit from employing IBM Cloud Security across their entire organization, but it may not be the most cost-effective or simplest option.
For newer companies who are untethered to on-premise investments, the public cloud options are appealing: instant scaling with comparatively little infrastructure overhead.
If you plan to be cloud native, IBM can certainly protect you, but why not explore something purpose-built for your desired environment. Cloud security companies like Zscaler can provide elegant solutions without introducing a single new appliance.
But what about companies using both AWS and Google Cloud? Their cloud security products are great, but what about the health of the entire infrastructure? Answering this question is even harder for hybrid deployments.
IBM Cloud Security is a complete multi-cloud and hybrid cloud security solution. No matter what technology or services you are currently using, they offer solutions that go right to the edge of your IT perimeter.
It is especially good for companies that know they will continue to need on-premises and private-cloud services in the future. This includes hospitals and banks, and other organizations with strict security, auditing, and compliance requirements.
The feature-rich services log all of the information you need to monitor cloud activity, and you have the capability to secure information to the highest standards.
Hospitals, for example, can ensure HIPAA compliance, even as they let patients, employees, and insurers access sensitive information from their own devices.
To sum it up, IBM Cloud Security is cutting-edge and comprehensive. It can serve as the entire security apparatus for your organization, or you can purchase services à la carte to enhance your existing protections.
For customers looking for a more hands-off approach with the shared responsibility of public cloud security, IBM offers Cloud Security-as-a-Service (CSaaS).
Under the CSaaS model, IBM absorbs some of the responsibilities that would ordinarily be left to the customer, like data security, network configuration, cloud monitoring, and so on. These managed plans give customers access to state-of-the-art solutions with minimal in-house overhead.
All of the power. None of the IT drama. Sounds pretty good.
Managed IBM cloud security plans aren’t free, but they may be less expensive than hiring all the people necessary to deliver a similar level of protection.

