The Ultimate Manual for CIS Benchmarks and Compliance
The Center for Internet Security (CIS) has done a terrific job compiling cybersecurity best practices that organizations of all sizes and industries can use to improve their cybersecurity posture. Most notably, the CIS Critical Security Controls provide a roadmap to help organizations protect themselves from the most common cybersecurity threats. For their part, the CIS Benchmarks give a baseline for securely configuring standard IT systems and products.
What are CIS Benchmarks and Compliance Anyway?
First, it’s essential to understand the CIS and its role in the cybersecurity landscape. The Center for Internet Security (CIS) is a non-profit organization comprised of volunteer cybersecurity experts from the government, private sector, and academia. The organization develops and promotes standards, policies, and best practices for improving cybersecurity readiness and response.
The organization also offers a range of programs, tools, and resources to promote cybersecurity best practices in government and the private sector. Many of these tools and resources are also free and available for anyone to use. Specifically, CIS Benchmarks provide a standard framework for calibrating and configuring the most common digital assets.
IT systems and products typically come with default configurations. However, these settings lean more towards ease of deployment than security. Therefore, the CIS Benchmarks provide organizations with consensus-driven configuration standards and best practices for securing vulnerable digital assets, including freshly installed and legacy assets.
There are over 100 benchmarks spanning more than 25 different vendor products. The featured products include the most commonly used systems such as Microsoft, Linux, Apple, Cisco, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google, Kubernetes, and IBM. Furthermore, the benchmarks cover seven primary areas, including:
- Server software
- Operating systems
- Mobile devices
- Desktop software
- Multi-function print devices
- Cloud providers
- Network devices
How CIS Benchmarks and Compliance Works
You can think of the CIS Benchmarks as an open-source project for developing security configuration best practices. First, a panel of cybersecurity experts convenes to develop a draft version of the benchmark recommendations. These experts are drawn from various sectors, including government, manufacturing, academia, and research. The preliminary panel develops, deliberates, and tests the draft before moving to the next stage.
Next, the CIS wider community receives the draft recommendations for appraisal. This wider community includes global cybersecurity and IT experts from various industries. Again, the community provides feedback and suggestions. Finally, the draft is amended before it is released to the public as the CIS Benchmarks.
Now the CIS Benchmarks take the form of a comprehensive PDF document with hundreds of pages. However, the document is logically structured to make it easier to implement the recommendations. For example, the document is broken up into sections such as Cloud Providers, Server Software, and Network Devices. So the Network Devices section outlines recommendations for configuring network devices and so on.
Each benchmark also has a logical structure. It starts with an overview of the benchmark, including the intended audience, definitions, and description. Next, the document outlines the rationale behind the benchmark and its impact on the organization. Finally, the document recommends specific actions and guidelines for implementing the benchmark.
The CIS Benchmarks PDF is available to download for free at the Center for Internet Security website. However, you’ll need to register an account with the CIS before you can download the document. The account is also free and only takes a few minutes to register.

Regarding CIS Benchmarks compliance, the CIS isn’t a regulatory agency. Therefore, it cannot enforce compliance with its Benchmarks. However, most organizations choose to comply with the benchmarks.
CIS Compliance makes sense since most major compliance frameworks reference the CIS Benchmarks as the gold standard. For example, organizations covered under the CMMC, HIPPA, and PCI-DSS regulations must comply with the CIS Benchmarks, directly or indirectly. Therefore, each recommendation also includes the steps for confirming CIS compliance.
Below are a few examples of how CIS Benchmarks and compliance work.
Example 1: Prioritizing CIS Benchmarks with Profiles
Securing system configurations is a complex problem even with the detailed guidelines provided in the CIS Benchmarks. For instance, it’s unclear where you should start hardening your system. The CIS Benchmarks categorize the system hardening process into two distinct Profiles.
These Profiles include Level 1 and Level 2. The Level 1 profile includes surface-level configuration recommendations. Organizations can implement benchmarks in this category reasonably quickly. These actions do not affect system performance, reduce functionality, or interrupt services.
It’s an excellent place to start for a business without a security policy. The recommendations in this level reduce the attack surface significantly while the company continues its normal operations.
Level 2 benchmarks offer security in depth. The recommendations in this category target organizations requiring tighter system security control. For instance, organizations covered by compliance frameworks like NIST, HIPPA, and PCI-DSS can significantly benefit from Level 2 recommendations.
However, Level 2 recommendations may cause some reduction in system functionality. Furthermore, these recommendations may cause unintended system conflicts if not implemented properly. That’s why many organizations prefer to outsource implementation to third-party security experts with the means to detect and remediate conflicts.
Example 2: Staying Current with CIS Benchmarks
The cybersecurity landscape shifts constantly. Old threats evolve, and new ones emerge, so secure system configuration is an ongoing process. The CIS regularly updates its benchmarks and releases new ones to keep up with current and emerging threats.
Fortunately, the CIS sends email notifications to its members every time there’s a new update. Simply signup to the CIS WorkBench to receive current news about CIS benchmarks. The portal also offers a platform where cybersecurity professionals can collaborate and network.
Finally, the CIS WorkBench offers a way to manage email notifications to avoid flooding your inbox with irrelevant material. For example, you can set your notification preferences only to receive relevant subscription messages.
Example 3: Tracking CIS Benchmarks Compliance
The CIS makes it very easy to test your compliance with its benchmarks. First, each recommendation provides instructions on how to audit your system for compliance with the specific recommendation. It’s an excellent place to start, but it isn’t a viable process for tracking compliance for tens of benchmarks.
For this, the CIS offers a free automated tool called the CIS-CAT. The tool scans your network to identify misconfigurations and other areas of non-compliance. Then, an administrator receives an alert about the non-compliance, complete with action steps for remediation.
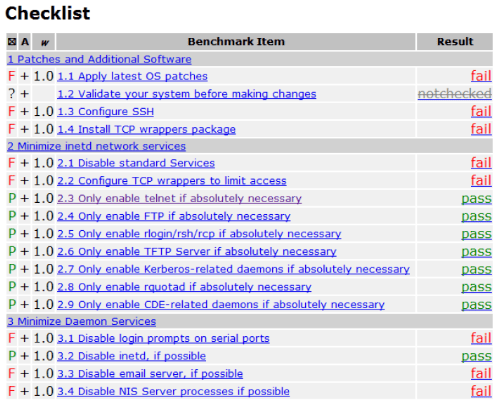
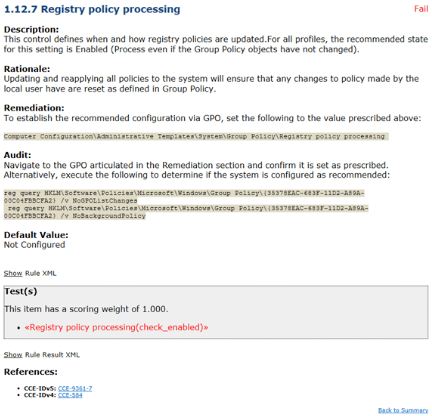
The tool is easy to use and offers granular control of compliance management. For instance, you can select the specific benchmark you want to scan and the Profile. You’ll receive a summary of the results and the suggested steps for compliance.
How to Get Started with CIS Benchmarks and Compliance
The CIS Benchmarks is an extensive document spanning thousands of pages. Each benchmark can potentially have hundreds of recommendations. So it’s easy to see why organizations may have difficulty complying with the standards. However, you can follow a few simple steps to guide your compliance processes.
Join the CIS WorkBench
The first step for CIS Benchmarks compliance is registering an account with the CIS WorkBench. Creating an account is free, and you’ll get all the resources you need for compliance. Plus, it only takes a few minutes to register your account.
The WorkBench also offers additional tools and resources besides the CIS Benchmarks. For example, you can also access CIS Controls from the WorkBench. You’ll also find supporting tools to help with compliance.
Unfortunately, you can only download the document in PDF format with a free account. However, you can register as a CIS SecureSuite member to download the benchmarks in additional formats such as Excel, Word, and XML. SecureSuite membership also provides access to more robust compliance tools you might need in the following steps.
SecureSuite offers four membership categories, including:
- End User
- Academic
- Non Profit
- SLTT Government
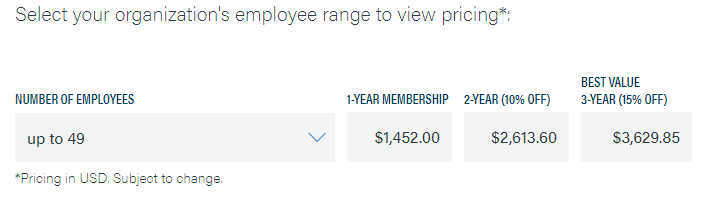
Most organizations fall under the End User category. The actual membership cost depends on the number of employees in the organization. However, the price starts at $1,452 per year for an organization with up to 49 members. You’ll also receive a 10% discount for a two-year membership and a 15% discount for a three-year membership.
Feel free to hold off signing up for the CIS SecureSuite membership until you’re sure you’ll need it. Your free account covers most fundamentals, including a basic compliance checking tool and the CIS benchmarks in PDF format.
Establish Your CIS Benchmarks Compliance Posture
The next step is assessing your organization’s standing concerning the CIS Benchmarks. Again, you could download the PDF document. However, manually going through each benchmark and testing for compliance isn’t feasible for most organizations.
Fortunately, the CIS provides a free tool for this step. It’s known as the CIS-CAT. There are two versions of the tool. The CIS-CAT Lite is free to download from the CIS WorkBench. You’ll use it to scan your network to check for non-compliance.
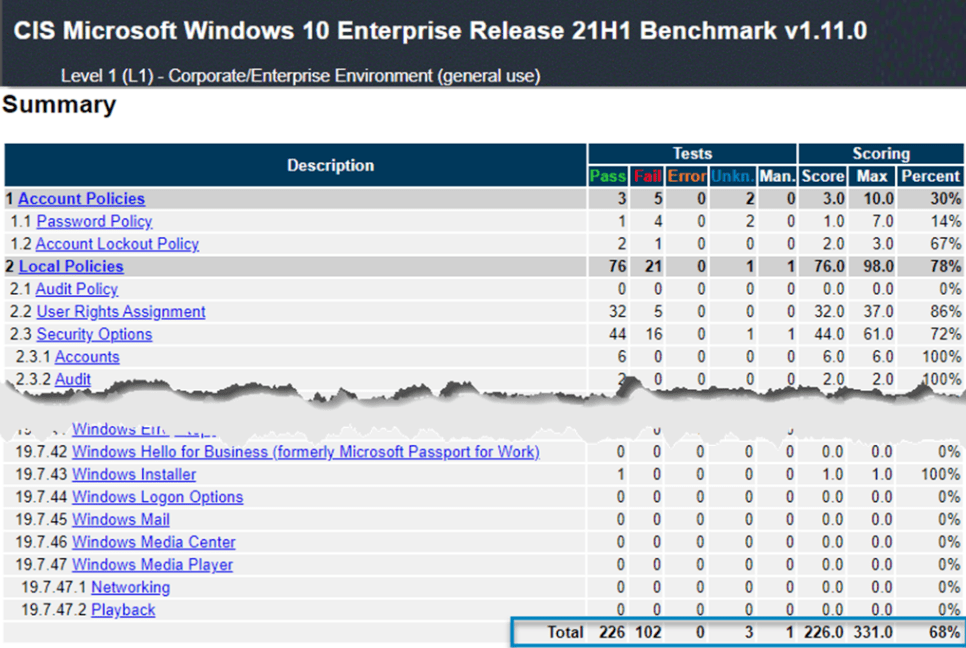
You can perform unlimited scans to get an idea of your compliance posture. The tool outputs an HTML report showing your compliance score from 1-100. The report also includes remediation steps to improve your security posture.
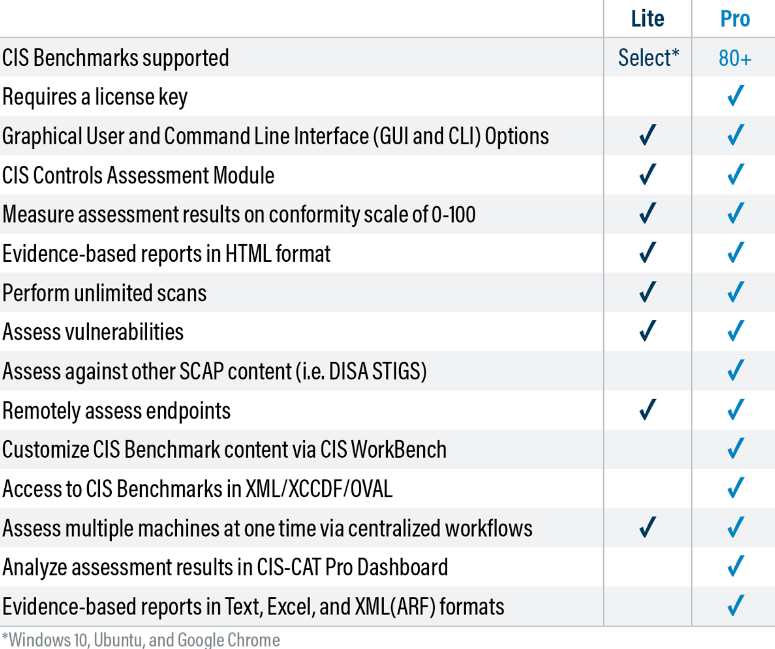
However, the CIS-CAT Lite has its limitations. For instance, this version limits supported CIS Benchmarks to Google Chrome, Microsoft Windows 10, and Ubuntu Linux. You also cannot customize the CIS Benchmarks.
The CIS-CAT Pro version unlocks these limitations. For instance, the Pro version supports more than 80 benchmarks. You also get additional functionality, such as analyzing the assessment results directly from the tool’s dashboard. It might be worth paying for the SecureSuite Membership, which comes with the CIS-CAT Pro version.
Prioritize CIS Benchmark Compliance Action Steps
The reports gathered in the previous section offer critical insights into your current compliance posture. Therefore, the next task is to prioritize the non-compliant benchmarks you should start with. A simple option is to start with the Level 1 Benchmarks.
Compliance with Level 1 Benchmarks should be relatively simple and won’t affect normal operations. Alternatively, you can create an IT task force to help prioritize the benchmarks based on severity, budget, resources, compliance-based requirements, business impact, or other criteria.
Automate CIS Benchmark Compliance
Again, manually testing and implementing CIS Benchmarks may not be feasible for most organizations. It’s a long, cumbersome, and error-prone process, especially for the more complex Level 2 benchmarks. So automation plays a crucial role in ensuring compliance with CIS Benchmarks.
The CIS offers tools known as Build Kits to help you automate this process. These tools differ depending on your environment. For instance, Build Kits for Windows are available as Group Policy Objects (GPO) but take the form of shell scripts for Linux and UNIX environments.
However, reviewing each non-compliant benchmark against the documentation is essential before deploying the Build Kit. The CIS Benchmarks are general recommendations that may not apply to your organization. The CIS even suggests customizing these benchmarks to suit your security policy.
It’s also necessary to first deploy the Built Kit in a test environment. This precaution will help you catch potential conflicts before applying them to your system. The Build Kit is only available to CIS SecureSuite Members.
Deploy CIS Hardened Images
Most modern organizations rely on the cloud for at least some computing power and workload. Specifically, virtual machine images provide organizations with an easy way to scale their computing power. However, ensuring that your cloud configurations comply with CIS benchmarks is equally essential. This is especially true for organizations that utilize the public cloud.
Theoretically, you could use the CIS Build Kits to harden your cloud environment. However, these tools are purpose-built for on-premise systems. There’s also an easier way to secure your cloud environment and comply with the CIS Benchmarks without much manual labor.
Most major cloud service providers offer CIS Hardened Images. According to the CIS Benchmarks, these virtual machines (VM) images are pre-configured. So you don’t have to spend additional time or resources configuring your VM images to meet your security needs.
For example, the AWS Marketplace offers free trials for specific instances of CIS Hardened Images, including Microsoft Windows, Ubuntu Linux, and Red Hat Enterprise. Simply visit your cloud provider’s marketplace and search for CIS Hardened Images.

