Global Cybersecurity Statistics 2021
A lot has happened in the past year, including a worldwide pandemic that completely disrupted the traditional workforce. Technology has played a crucial role in helping the world to adapt to the new reality of remote work. However, these changes have also brought about unique cybersecurity concerns, which we will detail in this post.
Top Cybersecurity Threats of 2021
2021 has been a unique year as far as cyber security is concerned. The global COVID-19 pandemic dramatically changed how we work, shop, and learn. The internet has been a lifeline in a world looking for a sense of normalcy in the face of restricted travel and outright lockdowns.
Cybercriminals have also been working overtime, leading to an upsurge in cyber threats in 2021. Consequently, 2021 has been a record year for cyber-attacks, already surpassing 2020’s total even before the year’s end.
Moreover, according to the Identity Theft Resource Center (ITRC), 2021 is set to record the highest number of publicly reported data breaches for a single year.
Given this grim introduction, here are the most prevalent cybersecurity threats of 2021:
Phishing
Phishing attacks are an all-time favorite for cybercriminals. Here, hackers trick users into downloading attachments or clicking links. Then, attackers can gain access to private databases, personal financial information, credit card credentials, and other types of sensitive information.

Phishing attacks top the list as the most common cyberattack in 2021. According to Google Safe Browsing, there were at least 2,145,013 registered phishing sites as of Jan 17, 2021. This figure is up 27% from Jan 19, 2020, when Google registered 1,690,000 phishing sites.
Phishing scams have also become more sophisticated and aren’t limited to email. For example, in smishing, the attack is delivered via SMS. Similarly, vishing attacks are delivered via voice calls.
Additional phishing statistics for 2021 include:
- The most targeted industries for phishing attacks in 2021 are financial institutions, social media, SaaS, payment, and E-commerce, respectively. (Source)
- 85% of phishing attempts in 2021 targeted user credentials. (Source)
- Phishing attacks account for 36% of all data breaches in 2021. (Source)
- 96% of phishing attacks originate from email. (Source)
- Companies implementing zero-trust security policies save $1.76 million in mitigated phishing attacks. (Source)
Ransomware
Ransomware attacks are malware that encrypts victims’ files, rendering them unusable. Then, attackers demand a ransom in exchange for restoring the files to their original state.
According to Coveware, a cybersecurity firm, the most common ransomware attacks in 2021 include Sodinokibi, Conti V2, and Lockbit. These malware variations accounted for 14.2%, 10.2%, and 7.5% of 2021 ransomware attacks, respectively.
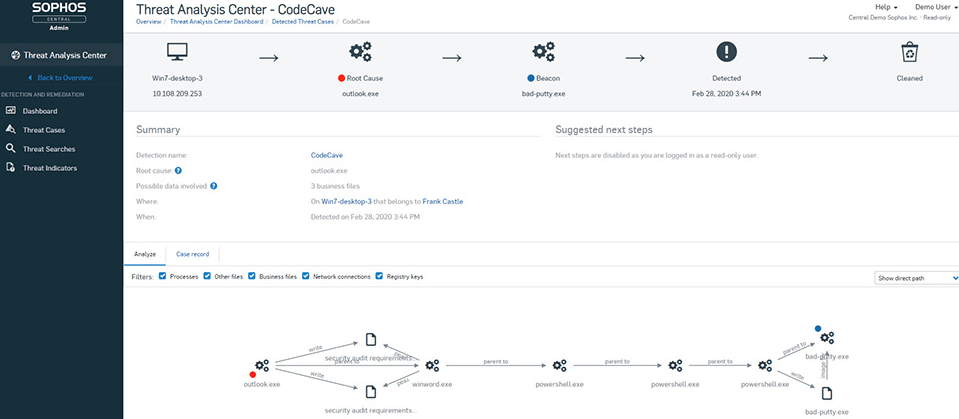
Although ransomware incidents dropped in 2020 and even further in 2021, there is still cause for concern. Larger organizations are at higher risk this year, accounting for 42% of attacks. This figure compares to 33% of smaller companies reporting ransomware attacks. (Source)
Additional ransomware statistics for 2021 include:
- Ransomware has already cost businesses $20 billion in 2021 in ransom payments. This figure is up from $11.5 billion by the end of 2019. (Source)
- The average recovery cost from a ransomware attack in 2021 is $1.85 million. This cost includes recovery expenses, lost opportunities, ransomware removal, and lost opportunities. (Source)
- The average hacker ransom demand in 2021 is $220,298. This figure is up 43% compared to $178,000 at the tail-end of 2020. (Source)
- However, the average ransom payment for small businesses is $5,900. (Source)
- Less than a third of ransomware victims pay hackers to decrypt their data. (Source)
IoT Device Attacks
Internet of Things (IoT) refers to physical devices connecting to the internet and sharing data. Generally, these are nonstandard devices that can grant users remote access and interact with other devices over the internet. Common IoT devices include fitness trackers, medical sensors, intelligent security systems, and smart refrigerators.
Notable IoT threats statistics for 2021 include:
- 48% of businesses report that they cannot detect IoT security breaches on their network. (Gemalto).
- 75% of cyberattacks target network routers. (Symantec)
- Most IoT attacks happen within the first five minutes of connecting to the internet. (NETSCOUT)
- Cyberattacks against IoT devices have grown more than 100% in 2021 (Source)
- There have been more than 1.5 billion IoT device attacks in the first half of 2021 alone. These attacks mostly attempt to build botnets, mine cryptocurrency, and steal data. (Source)
Cryptojacking
Cryptojacking refers to when hackers hijack a victim’s personal or work computer to mine cryptocurrency. Cryptocurrency mining requires immense computer resources, so hackers may target unwitting internet users and hijack their processing power.
Unfortunately, cryptojacking cases are on the rise in 2021. In this case, hackers send malicious links that unknowing users click on, giving the hackers remote control of the victim’s computer. Then, the cybercriminals inject malware into the victim’s computer to secretly mine cryptocurrencies in the background. The process can use up as much as 70-80% of a computer’s processing power.
Cryptojacking malware, known as crypto miners, accounted for 41% of all detected malware in 2020. This trend is said to continue well into 2021. Kaspersky reported at least 432,171 cases of cryptojacking in the first quarter of 2021. (Source)
This spike in cryptojacking has been largely attributed to the increased value of cryptocurrency across the board. Historically, crypto miners increase during such booms, and cryptojacking incidents go down when crypto value plummets.
Notable Examples of 2021’s Notable Cyber Breaches
2021 has been a busy year for cybercriminals. Some of the year’s noteworthy cyberattacks and breaches include:
Example 1: Twitch
5 Billion Records Leaked
Twitch, the Amazon-owned streaming service took to Twitter on October 6th, 2021 to announce a significant data breach. According to the BBC, the breach resulted in more than 100GB of leaked data.
The stolen data was later posted publicly on 4chan. Some of the stolen information included internal company documents, user data, security tools, and the service’s proprietary source code. Famously, payment information for Twitch elite gamers was also posted publicly.
The hack and subsequently leaked information are attributed to a “hacktivist” who was unhappy about the platform’s allegedly toxic community. There’ve been multiple incidents of malicious Twitch users developing bots to flood chatrooms with hateful messages. These attacks mostly targeted elite streamers on the platform.
Consequently, search engine queries for deleting Twitch rose 733% soon after the breach announcement.
Example 2: The Pandora Papers
11.9 Million Documents Leaked
The Pandora Papers have been dubbed the most significant offshore data leak in history. The hack targeted the rich and powerful to expose their financial secrets. The leak included files from financial companies used by the ultra-wealthy to create trusts and offshore structures in tax havens.

The leak included the financial secrets of more than 35 world leaders and 300 public officials in more than 90 countries. Leaked documents included share certificates, incorporation records, memos, emails, and compliance reports.
The Pandora Papers were leaked to the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists (ICIJ), revealing tax avoidance, hidden wealth, and even money laundering. It is worth noting that running secret companies or using offshore services is not illegal, but these services have been used to launder money, avoid taxes, and divert money.
Example 3: Astoria Company Database Breach
30 Million Individuals Impacted
Astoria Company, a lead generation company, was the victim of a data breach on January 26, 2021. The breach affected more than 30 million users of the company’s database. Astoria Company runs a network of websites that collect information on persons looking for payday loans, discounted car loans, and medical insurance.
Users volunteer personal information to Astoria’s network of websites. This information is later sent to partner sites such as loan agencies. Finally, Astoria makes its money through pay-per-lead referrals.
A threat intelligence team became aware of Astoria’s data breach. The stolen information was later listed for sale on the Dark Web. This information included people’s:
- Name
- Date of Birth
- Email address
- Physical Address
- IP Address
- Mobile Phone
Other leaked data included people’s complete bank account information, social security numbers, and medical records. The breach resulted from malicious scrips on the company’s website, allowing anyone access to the database from a public URL. More than 30 million Americans were affected by the breach.
(Source)
2021 Cybersecurity State of Preparedness Statistics
The cybersecurity statistics for 2021 are grim so far. The obvious question is how well organizations are prepared to defend themselves against cyberattacks. According to Axio’s 2021 State of Ransomware Preparedness report, the outlook isn’t too bright either.
The report identifies several key areas where organizations are failing to implement and sustain basic cybersecurity practices, including:
Privileged Access Management – It appears that many organizations lack fundamental oversight and control over privileged credentials and access. Poor credential management is the most significant risk factor for cyberattacks. Unfortunately, many organizations do not take enough precautions to protect privileged credentials.
Exposure to Third-Party Risk – Most organizations rely on external partners to provide critical services. Many times, these third parties require network access for convenience and efficiency. Unfortunately, this setup means that the organization has less direct control over its network security.
Worst still, 29% of the survey’s respondents admitted that they do not vet the external party’s cybersecurity position before allowing access to their network. In short, the inherited risk from external partners is a severe cybersecurity concern in 2021.
Basic Cyber Hygiene – Cyber hygiene means implementing basic practices and controls to secure a company’s data, network, and assets. Most of these practices are a low investment with potentially high rewards.
However, poor cyber hygiene is a worrying trend in 2021. For example, 69% of organizations report unlimited internet access for Windows domain controller hosts. This trend is worrying since domain controllers are a favorite avenue for hackers to spread ransomware or other attacks throughout the organization.
Network Monitoring – Network monitoring is indispensable for identifying and defusing cyberattacks before they occur. However, a worrying number of organizations do not monitor their networks for anomalies that may indicate an imminent attack. Even more worrisome, a significant number of organizations haven’t invested in basic network controls.
For example, 64% of companies do not monitor their networks for suspicious data transfers or network processes that consume disproportionate resources.
Other noteworthy statistics from the 2021 State of Ransomware Preparedness Report include:
- Nearly 80% of organizations have either not implemented or have only partially implemented a privileged access management solution.
- Only 50% of companies conduct annual user awareness training for employees.
- Only 42% of organizations log actions executed using privileged credentials.
- Only 39% of companies monitor for irregular use of privileged credentials.
- Only 26% of companies restrict command-line scripting tools by default.
- 60% of organizations do not maintain updated records of external parties with access to their network.
Cybersecurity Trends for 2021
There is much to be done to prepare for cyberattacks adequately. So, what are organizations doing in 2021 to fend off cyber breaches? We can look at some of 2021’s cybersecurity trends to get answers to this question.
Transition to Zero-Trust Platforms
For one, we are likely to see a transition to Zero-Trust Network Access (ZTNA). These platforms are likely to replace Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) for two main reasons. First, VPNs are proving inadequate for stopping phishing attacks, which are on the rise. (Source)
Secondly, the COVID 19 pandemic has necessitated working away from a centralized office. By contrast, home offices tend to have less secure routers, firewalls, and access management. This situation is hardly surprising in the absence of a dedicated IT security team.
Therefore, network security is a concern more than ever before. The Zero-Trust policy is founded on the premise that there is no such thing as a trusted source. Therefore, organizations are keen to create a framework of enforced cyber hygiene.
According to the National Cyber Alliance, 60% of businesses will transition from VPNs in favor of ZTNA by 2023. (Source)
More Widespread Use of Multi-Factor Authentication
Strong passwords have long been a standard cybersecurity best practice. But more organizations are waking up to the reality that strong passwords aren’t enough to ward off cyberattacks. Many businesses are turning to Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to bolster cybersecurity.
MFA requires users to provide two or more verification factors. For example, a user may be required to enter their password and enter a unique code sent to their mobile phone.
According to Google, 2FA alone can stop three-quarters of targeted attacks, 96% of bulk phishing attacks, and 100% of all automated attacks.
Rising Cloud Security Threats
Today’s remote workforce is heavily reliant on cloud services. These services come with several benefits, including cost savings, efficiency, and scalability. According to a Cybersecurity Insiders report, 76% of companies use two or more cloud providers. Furthermore, 92% of organizations host at least part of their IT environment in the cloud.
However, cloud services also come with unique security threats and vulnerabilities. For example, poorly configured cloud settings may lead to security vulnerabilities such as unauthorized access, data breaches, and account hijacking.
Cloud services adoption also raises additional security issues, including misuse of personal devices, weak passwords, multiple potential entry points for hackers, and regulatory compliance issues.
The concern about cloud security threats is far from mere fearmongering. A whopping 79% of companies have experienced a cloud data breach in the past 18 months, according to a 2021 IDC survey.
Increased Use of Artificial Intelligence
Increased use of cloud services, remote working, and widespread adoption of IoT devices contribute to the rise in cyberattacks. Security experts are hard-pressed to develop practical solutions to increasingly more sophisticated cyber threats.
We will likely see more widespread AI and machine learning to bolster security infrastructure. Artificial Intelligence brings a promising capability to the fight against cybercrime. For example, AI can analyze large mounds of at-risk data quickly. Additionally, this technology has proved its worth in natural language processing, automatic threat detection, and automating security systems.
Sadly, the opposite is also true. Hackers are already automating their attacks. Unfortunately, there is every reason to believe that this trend will continue to grow. These automated attacks will also get more targeted, effective, and complicated.
(Source)
Suggested Further Reading
Axio 2021 State of Ransomware Preparedness Report

