The Ultimate Manual to GitHub Copilot
Writing code is often a tedious and time-consuming task. Modern developers are always looking for new ways to improve productivity, accuracy, and efficiency with programming.
Automatic code generation tools like GitHub Copilot can make this possible.
What is GitHub Copilot Anyway?
Branded as an “AI pair programmer” and coding assistant, GitHub Copilot uses artificial intelligence to auto-generate code in your editor. It’s available as an extension for Visual Studio Code, the JetBrains suite of IDEs, and Neovim.
But GitHub Copilot is more than just an autocomplete solution. Based on context clues from the code you’re writing, Copilot suggests lines and even entire functions. It’s a faster and easier way for developers to create tests, explore APIs, and solve problems without constantly searching for answers elsewhere.
Once you start working with the GitHub Copilot plugin, the tool automatically adapts to the way you write code.
Copilot is fast and works seamlessly with your workflow as you’re writing code. When you start to get the hang of it, a single click on your keyboard will autocomplete the code you need.
Unlike similar solutions on the market, GitHub Copilot gives you complete control—hence the name. You can accept or reject the code, manually edit suggestions, and cycle through alternative suggestions. Since the tool adapts to your coding style, the suggestions it gives you in the future will continue to get smarter.
How GitHub Copilot Works
GitHub Copilot is powered by OpenAI Codex. The auto-generated suggestions come from the context within the file, like function names, code comments, docstrings, file names, cursor position, and more. Based on this information, Copilot suggests code snippets that developers can accept by simply pressing the Tab key on their keyboards.
The AI tool understands TypeScript, Python, JavaScript, Ruby, and dozens of other common languages.
That’s because the AI suggestions are coming from open-source code within GitHub’s public repositories. It analyzes that information and then tries to find the best possible solution based on what you’re writing.
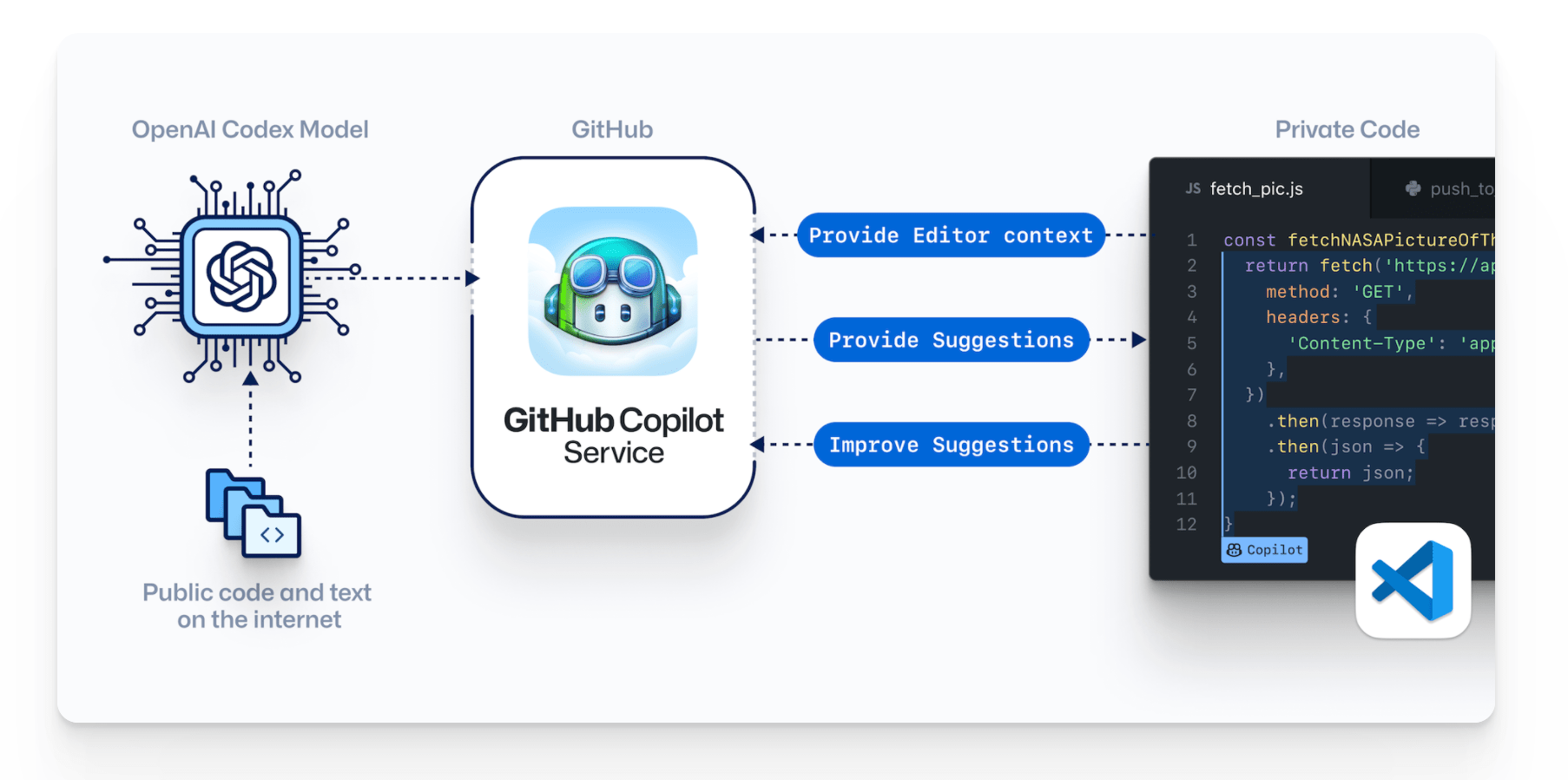
A standout of GitHub Copilot is its ability to understand natural language. This includes programming languages and human languages alike.
It’s worth noting that GitHub Copilot does not write perfect code. The tool does its best to try and understand the developer’s intent. But, you’ll notice that some of the suggestions don’t always work or even make sense.
GitHub Copilot doesn’t test any of the code it’s suggesting to you. Those suggestions may not compile or run. So you still need to carefully review and test the code before you assume it’s usable.
To get the most out of GitHub Copilot, you should segment your code into smaller functions. Make sure you’re writing good comments and docstrings as you’re working. Always use meaningful names for function parameters, as this will make it easier for Copilot to understand your intent.
GitHub Copilot seems to have the most significant impact on developers working with unfamiliar frameworks and libraries. Rather than searching through open-source documentation on your own, Copilot can navigate this for you within seconds.
Overall, GitHub Copilot is probably the best autocomplete tool on the market. It provides developers with lots of different ways to solve problems beyond basic suggestions. The range of suggestions you’re getting for a code snippet is great, and you likely won’t need to use Stack Overflow to find answers.
But, it’s important to understand that GitHub Copilot is just a tool. It’s not even close to replacing the need for human developers. You cannot rely on Copilot alone, and it’s still on the developer to accept the suggestions and make changes.
Let’s take a closer look at different examples that Copilot can be used for. These examples will help you better understand the tool’s functionality and versatility:
Example #1: Convert Comments to Code
One of the coolest features of GitHub Copilot is its ability to take your comments and turn them into code. Just create a comment that describes the logic you need, and Copilot will automatically generate suggestions for you.
Here’s what that looks like:
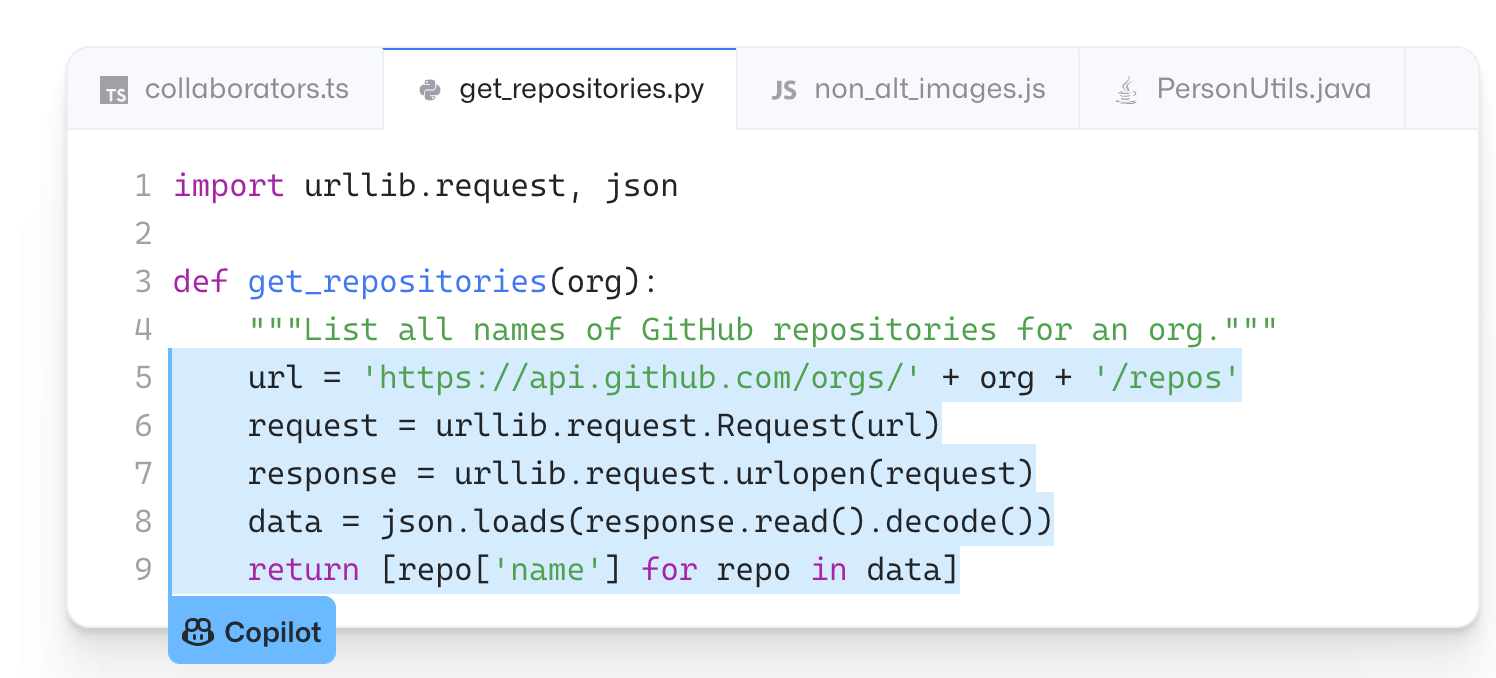
In this case, the comment simply says, “List all names of GitHub repositories for an org.”
Copilot immediately generated a suggestion. If you were writing this code, all you’d need to do is click Tab to accept it. As you can see, this comment was written in plain English. GitHub Copilot still understood the intent and made the appropriate suggestion.
This relates to something that we mentioned earlier—always write good comments and docstrings. If your comments are written in an unnatural language, it can be tough for Copilot to understand the appropriate intent.
Example #2: Autofill Repetitive Code
GitHub Copilot is an ideal way for developers to speed up the way they write repetitive code. If you’re writing large blocks of boilerplate code, you just need to input a few examples of the pattern. Then Copilot will handle the rest.
Here’s a really simple example to show you how this works:
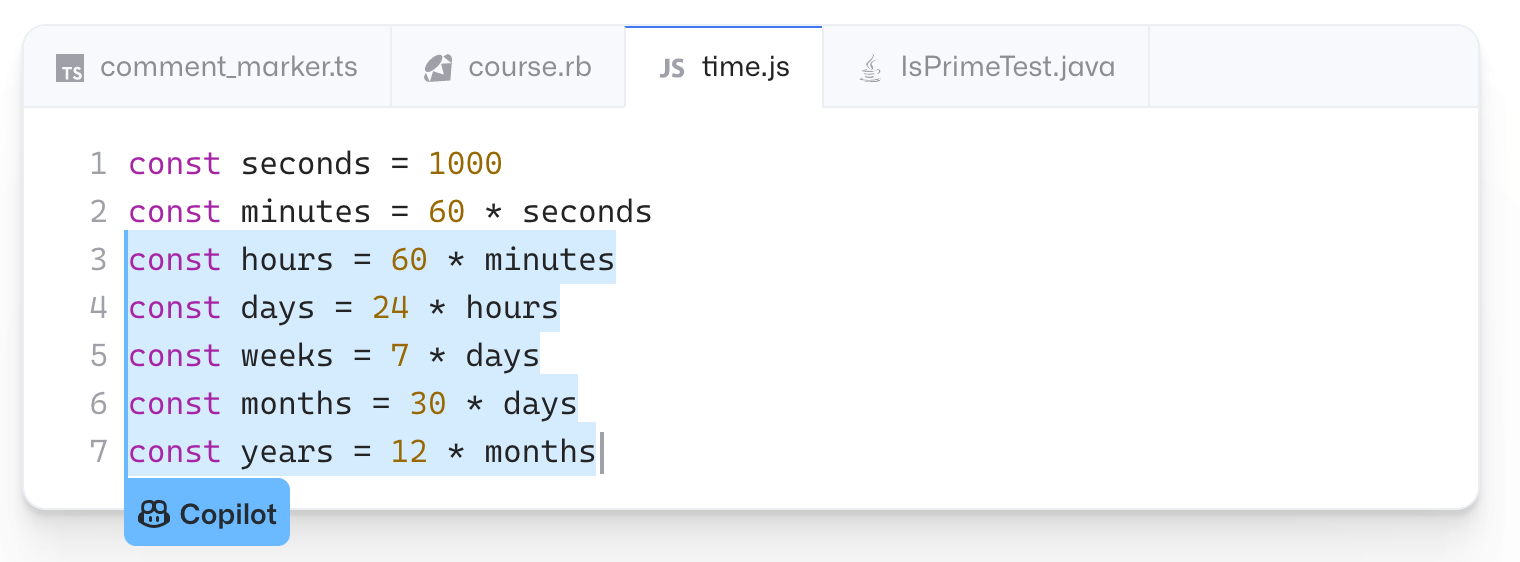
In this example, the constant variable starts with seconds. Once the second line shows the const as minutes multiplied by seconds, Copilot recognizes the pattern and auto-completes the code for hours, days, weeks, months, and years.
These five additional lines of code can be written with a single click. At scale, this will shave a ton of time off your programming, especially for larger blocks.
Example #3: Run Tests
As previously mentioned, GitHub Copilot doesn’t test the code it’s suggesting. But with that said, you can use it to suggest tests matching your code implementation.
It’s a great way to quickly import a test unit package. Here’s an example that generated a test from a plain English comment:
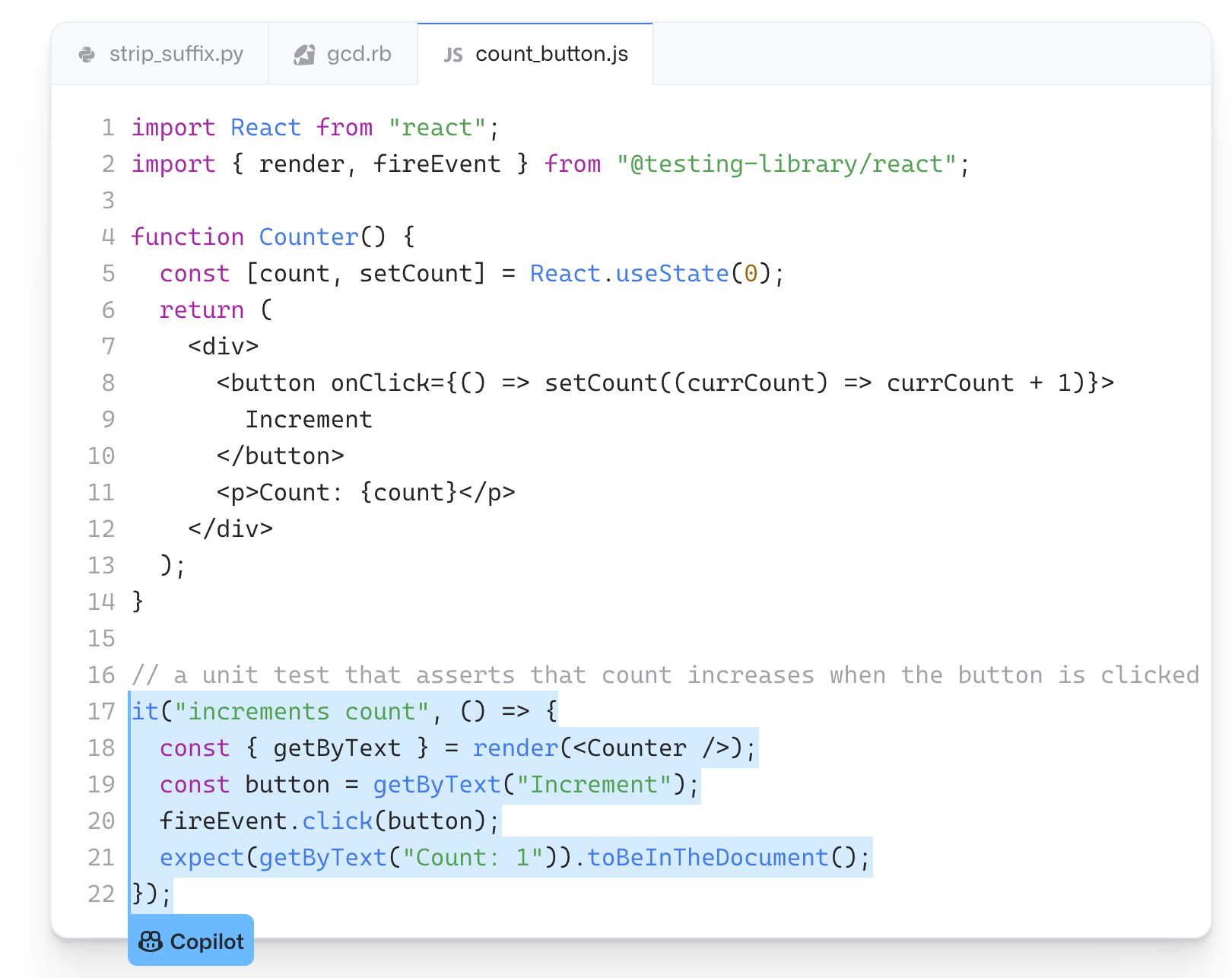
You’ll still need to verify that the code makes sense, but it’s a faster alternative to completing this code on your own.
Example #4: Navigating Unfamiliar Territory
This particular use case is arguably Copilot’s best function. It’s a great way for developers to navigate the waters of an unfamiliar language or framework.
For example, let’s say you wanted to draw a scatter plot. The way you would write this code would vary significantly based on the programming language you’re using. Here’s an example of what that code would look like in Python:
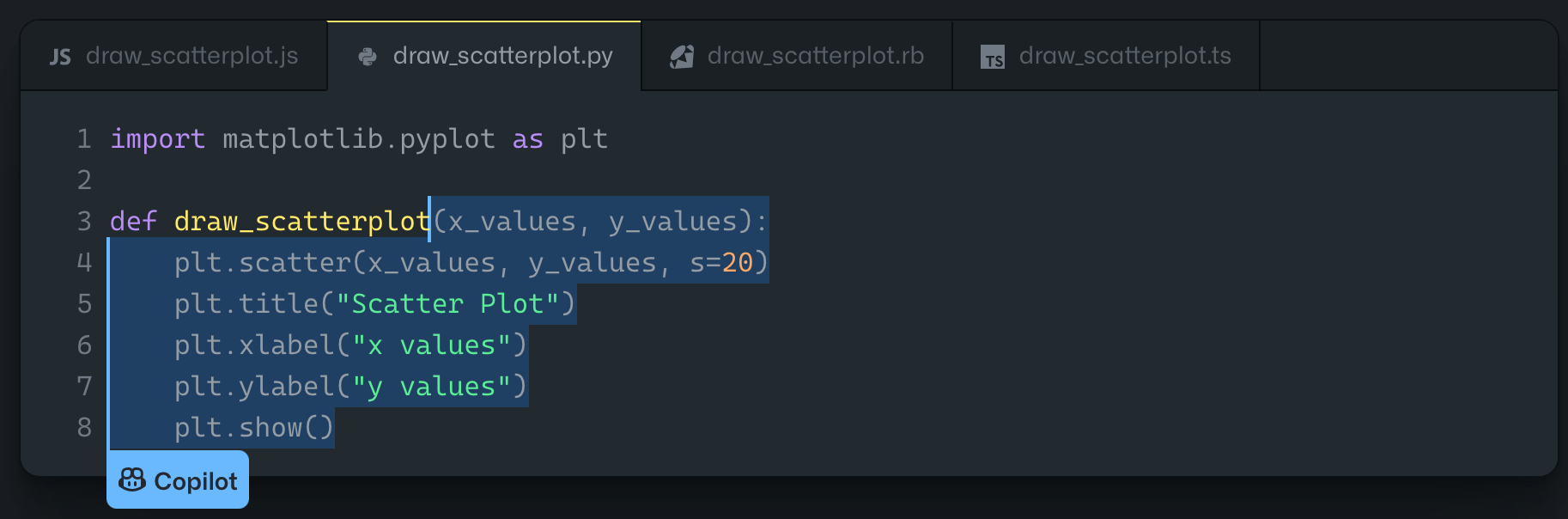
Even if you’re experienced and comfortable writing in Python, this autocomplete function will still save you time.
But for argument’s sake, let’s say you needed to write a scatter plot in JavaScript—but you’re not very familiar with this programming language. In this case, GitHub Copilot has you covered. Look at what it can generate for you here:
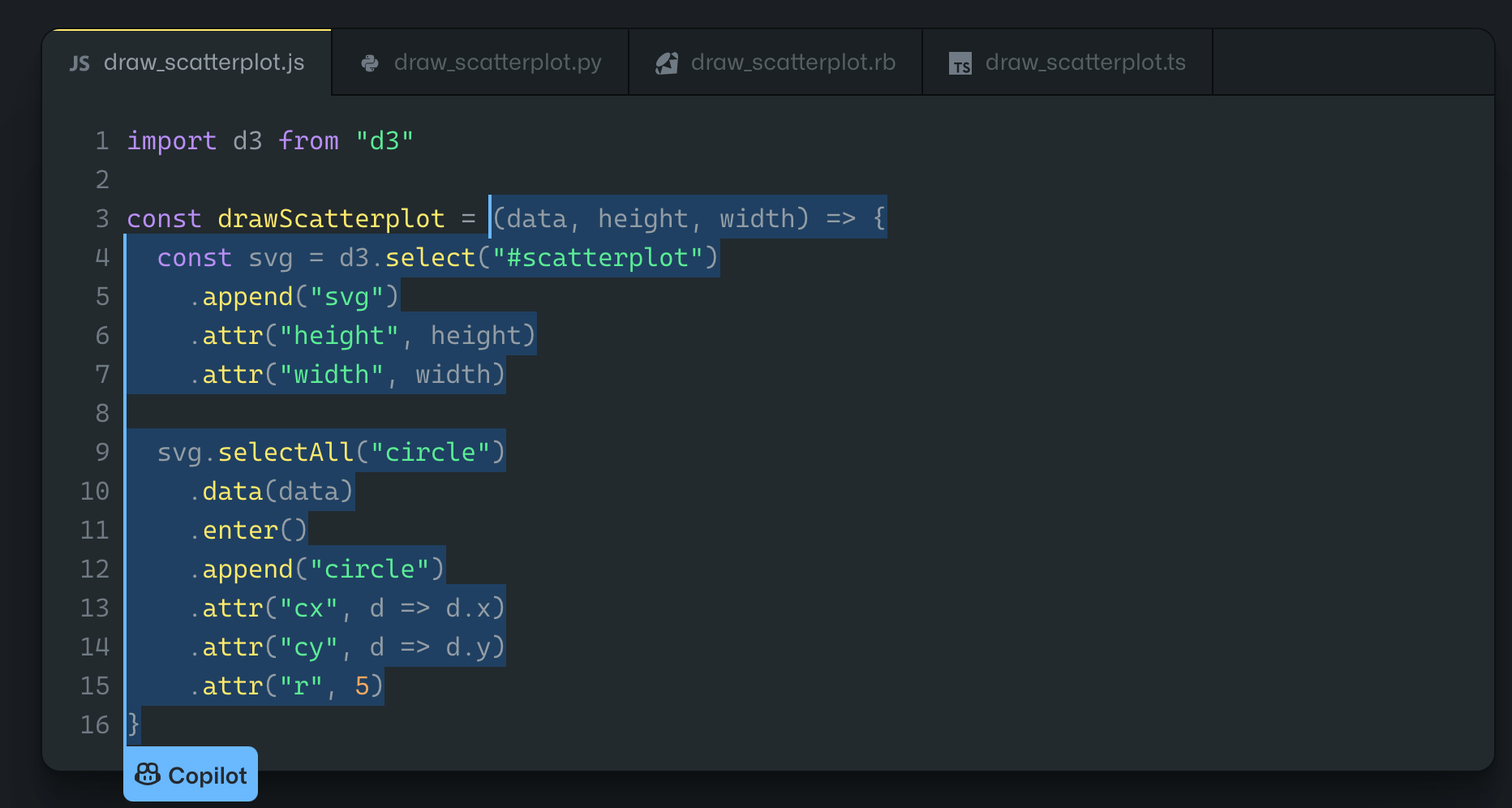
To write this without Copilot, you’d be forced to manually search through public repositories for examples. Or maybe you’d use a resource like Stack Overflow to find your answers. But both of those alternatives are tedious and time-consuming.
Experienced developers love to use Copilot when navigating unfamiliar languages. Even if Copilot’s suggestions aren’t perfect, it can still get the basic syntax right. It will also point you in the right direction when it comes to common idioms, library functions, and more. Copilot can even be used as a self-help teaching tool for programmers.
Example #5: Creating an Application Entirely With Copilot
In addition to the broad examples of Copilot’s capabilities, we wanted to find a real-life success story of someone who used Copilot to create something. We found an excellent case study on LogRocket, written by a UK-based software engineer.
Let’s take a closer look at the highlights of this story.
The programmer, Evgeny Klimenchenko, decided to create a simple test application to see if Copilot could handle the project. The app was a random quote generator that also displayed the quote’s sentiment.
To truly test Copilot, Klimenchenko told himself that he would not search Google or Stack Overflow for solutions. He would rely solely on Copilot’s suggestions. No new code would be written by him either. But, he allowed himself to write variables, comments, and function names, and make edits to the suggestions.
Within one week, Copilot helped Klimchenko create a simple quote-generating application. It’s very basic and not really useful for anything specific. However, the case study proved the Copilot functions as advertised.
How to Get Started With GitHub Copilot
If it’s your first time using GitHub Copilot and you’re not sure what to do, you’ve come to the right place. The steps below will not only tell you how to use GitHub Copilot, but they’ll also set you up for success. Here’s what you need to do:
Step 1: Narrow Down Your Use Case and Goal
Technically, this isn’t a requirement for using Copilot. But if you’re just getting familiar with the tool, it’s definitely in your best interest to do so.
Don’t just approach GitHub Copilot with a “let’s see what happens” mentality. This will likely overwhelm you, and you won’t get the most out of the tool’s functions.
For example, you might decide to use GitHub Copilot strictly for auto-filling boilerplate code. Everything else you’ll write on your own as usual. But when you encounter situations where there’s an option for you to autocomplete repetitive lines, you can take advantage of Copilot.
Or maybe you’re on the complete opposite end of the spectrum. Instead of using Copilot to assist with your regular programming work, you may want to run an experiment similar to the case study we discussed earlier.
Many developers take advantage of GitHub Copilot when they’re working in an unfamiliar programming language. Copilot will help them get the syntax right and get a basic understanding of library functions.
Once you’ve identified how you plan to use Copilot for your next project, the rest of these steps will be much easier.
Step 2: Install the GitHub Copilot Extension
GitHub Copilot doesn’t come standard with any editors. So you’ll need to add the extension before you can start using it.
Here are the ways you can use to install Copilot, depending on your preferred editor:
- GitHub Copilot — Visual Studio Code Marketplace
- GitHub Copilot — JetBrains Marketplace
- Neovim Plugin for GitHub Copilot
We think the GitHub Copilot extension works best in Visual Studio Code. That’s because Visual Studio Code also works in GitHub Codespaces.
After you install the extension, Copilot will prompt you to authorize the plugin by signing into GitHub. Once authorized, you should automatically be sent back to the editor. If the extension has been installed correctly, you should see the Copilot icon in your status panel.
Step 3: Learn the GitHub Copilot Keyboard Shortcuts
You should get familiar with common keyboard shortcuts for GitHub Copilot. They’ll vary slightly, depending on whether you’re using macOS, Windows, or Linux.
Here are the ones you should know:
- Accept inline code suggestion — Tab
- Dismiss inline code suggestion — Esc
- Show next suggestion — Alt + ] or Option (⌥) + ]
- Show previous suggestion — Alt + [ or Option (⌥) + [
- Trigger suggestion — Alt + \ or Option (⌥) + \
- Open 10 suggestions in a separate pane — Ctrl + Enter
Keep these close by as a quick reference as you’re working.
Step 4: Start Writing Your Code and Review the Suggestions
Now you just need to start working like you normally would.
As you’re writing, you’ll start to see GitHub Copilot automatically suggest options to autofill based on the context. It’s up to you whether or not to accept or reject those options.
If you don’t like what Copilot is providing, you can always see other suggestions to see if those options are more relevant. Copilot definitely takes some getting used to, but you’ll get the hang of it the more you use it.
Step 5: Make Edits and Test Your Code
As previously mentioned, Copilot isn’t perfect. So you can’t just take the suggestions at face value and assume everything is perfect.
You’ll likely need to make some minor edits to the code. As always, you should always run tests before committing the code to your project.
GitHub benchmarked Copilot’s accuracy by reviewing a set of Python functions in open-source repositories. They eliminated the function bodies and prompted Copilot to fill them in. Copilot got the functions right 43% of the time on its first attempt. When Copilot was allowed 10 attempts, the code was right 57% of the time.
If this benchmark is any indication of how Copilot will perform as you’re using it, there’s a good chance you’ll need to make at least some minor edits to the suggestions.
GitHub Copilot Plans and Pricing
GitHub Copilot has transformed into an AI coding assistant that enhances developer workflows.
In spring 2023, GitHub launched Copilot X, a “readily accessible AI assistant.” According to the company, it adopted OpenAI’s GPT-4 model, and introduced chat and voice for Copilot, bringing Copilot to pull requests, the command line, and docs to answer questions on projects.
This enabled “context-aware conversations.” Developers could ask GitHub Copilot to explain a piece of code, fix an error, or even generate unit tests.
Now, GitHub Copilot has taken its AI assistant to the next level and offers three plan options for individuals, businesses, and enterprises. We’ll briefly go over each plan below.
Copilot Individual
- Who’s it for: Individual developers, freelancers, students, and educators who want to code faster.
- Cost: $10 per month or $100 per year.
- Free for verified students, teachers, and maintainers of popular open-source projects.
What’s included:
- Chat
- Unlimited messages and interactions
- Context-aware coding support and explanations
- Debugging and security remediation assistance
- Code completion
- Real-time code suggestions
- Comments to code
- Smart actions
- Inline chat and prompt suggestions
- Slash commands and context variables
- Commit message generation
- Supported environments
- IDE, CLI, and GitHub Mobile
- Management and policies
- Public code filter
Copilot Business
- Who’s it for: Organizations ready to improve engineering velocity, code quality, and developer experience.
- Cost: $19 per user per month.
What’s included:
- Chat
- Unlimited messages and interactions
- Context-aware coding support and explanations
- Debugging and security remediation assistance
- Code completion
- Real-time code suggestions
- Comments to code
- Smart actions
- Inline chat and prompt suggestions
- Slash commands and context variables
- Commit message generation
- Supported environments
- IDE, CLI, and GitHub Mobile
- Management and policies
- Public code filter
- User management
- Data excluded from training by default
- IP indemnity
- Content exclusions
- SAML SSO authentication
Copilot Enterprise
- Who’s it for: Companies that want to customize GitHub Copilot to their organization and infuse AI across the developer workflow.
- Cost: $39 per user per month.
What’s included:
- Chat
- Unlimited messages and interactions
- Context-aware coding support and explanations
- Debugging and security remediation assistance
- Conversations tailored to your organization’s repositories
- Answers based on your organization’s knowledge base
- Access to knowledge from top open-source repositories
- Pull request diff analysis
- Web search powered by Bing (beta)
- Code completion
- Real-time code suggestions
- Comments to code
- Fine-tuned models (coming soon as an add-on)
- Smart actions
- Inline chat and prompt suggestions
- Slash commands and context variables
- Commit message generation
- Pull request description and summarization
- Supported environments
- IDE, CLI, and GitHub Mobile
- GitHub.com
- Management and policies
- Public code filter
- User management
- Data excluded from training by default
- IP indemnity
- Content exclusions
- SAML SSO authentication
- Requires GitHub Enterprise Cloud
For more information on GitHub’s AI assistant, visit here.

